This is lesson #2 in my thyroid beginner series which is primarily designed for those who are building a foundation of knowledge in thyroid dysfunction or for those who have recently been diagnosed.
Today we will be discussing why there is so much controversy surrounding thyroid treatment and why it can be difficult to get your doctor “on board”.
Watch the video above for more info or read the text below if you prefer as well!
Please leave your questions in the comment section below so I can go over them in the next video!
Thyroid Controversy: Integrative vs Conventional Treatment
Why are so many thyroid patients unhappy with their current treatment?
Is it possible that our current approach or understanding of thyroid management is flawed?
I think this answer can be addressed by simply looking at how we approach and manage thyroid dysfunction and comparing that to other ways that we look at hormone imbalance in the body.
Patients often find themselves in an unfortunate situation:
They have been diagnosed with thyroid issues and are experiencing thyroid symptoms even though they are already taking thyroid medication.
If you fall into this situation you might be asking yourself this question…
How is it possible for me to feel so terrible when my Doctor keeps telling me that my thyroid is “normal”?
And this is the thyroid controversy in a nutshell and it comes down to how Doctors look at and manage the thyroid.
This approach to thyroid management has left thyroid patients frustrated which leads them to seek help on the internet, on forums, and on Facebook groups.
With this in mind let’s take a look at how conventional doctors approach thyroid management and compare that to integrative doctors.
DOWNLOAD FREE RESOURCES
Foods to Avoid if you Have Thyroid Problems:
I’ve found that these 10 foods cause the most problems for thyroid patients. Learn which foods you should avoid if you have thyroid disease of any type.
The Complete List of Thyroid Lab tests:
The list includes optimal ranges, normal ranges, and the complete list of tests you need to diagnose and manage thyroid disease correctly!
How Conventional Doctors Look at Thyroid Treatment
The standard and conventional approach, the approach that is taught in medical schools and residencies, is actually quite simple.
I’ll outline it to you below (this is the way that I was taught and the way that most doctors are taught):
- If thyroid disease is suspected then check for a lab known as the TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone).
- If the TSH is high (defined as outside of the lab reference range) then initiate treatment.
- Treatment should always be done with T4-only thyroid medications such as Levothyroxine, Synthroid, or Tirosint.
- Adjust medication until the TSH is somewhere around 1.0 to 2.0.
- Any other symptoms related to thyroid disease (such as fatigue, weight gain, depression, constipation, cold skin, etc.) must be related to some other cause if the TSH is normal.
- Make adjustments to thyroid medication based on the TSH which is tested every 2-3 months.
The main problem with this approach is that it is too rigid to allow for variability among patients.
For instance:
How is it possible that all thyroid patients can do well on one medication?
Even when treating diseases such as cholesterol and high blood pressure Doctors have several sets of medications (1) that they will use and play around with but when it comes to the thyroid they are set on using one medication.
Is it possible that some patients differ in their ability to utilize thyroid medication?
Some patients may react to the fillers or dyes in certain medications or vary in their ability to absorb medication from gastrointestinal issues.
Problems such as lactose intolerance, Celiac disease or SIBO (2) can all influence how the body absorbs these medications.
Is it possible that genetics may play a role in which medication works best for each person?
Doctors have no problem ordering genetic tests which outline how you metabolize anti-depressants, but they fail to consider that individuals can vary in how they metabolize hormones in the body.
It is well known that individual genetics impact the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of medications and hormones in the body (3)!
These are just some of the reasons that taking such a rigid approach doesn’t make sense from a logical standpoint, but there are other reasons as well.
Does Focusing on the TSH Make Sense?
The reliance upon TSH as a sole marker for thyroid function may not make sense when you compare it to other pituitary hormones and how Doctors treat those issues.
To understand this let’s briefly discuss what TSH is and how it works:
TSH is known as thyroid stimulating hormone and it is secreted by the pituitary gland in your brain.
TSH acts directly on the thyroid gland to stimulate the release of thyroid hormone (4).
So the higher your TSH is the more “stimulation” your thyroid gland gets and the more hormone your produce.
But TSH isn’t the only hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland which acts in a similar way.

But what’s interesting here is that whenever we look at other hormones, such as testosterone, we don’t care what the pituitary stimulating hormone level is, we care about the level of the hormone in the body (5)!
For instance:
If you feel that you have low testosterone in your body would it make sense for your Doctor to check your pituitary stimulating testosterone hormone or to directly check testosterone levels in the body?
Logically, it makes sense to check for the hormone.
But that’s not what we do with the thyroid.
Instead of looking at the hormone levels in your body, we check for the pituitary-stimulating hormone TSH.
And instead of adjusting the dose based on how much hormone is in your blood, conventional doctors adjust it based on the TSH.
But there’s a problem with that:
Studies have shown that patients who are treated with T4 thyroid medication to a “normal” TSH still have lower than normal free thyroid hormone levels which may account for the trouble that many patients experience.
This can largely be solved with the use of both T4 and T3, but physicians still refuse to use these medications.
But back to the way that physicians normally dose and look at other hormones in the body for a minute.
Consider these examples:
- Birth Control Medication – Birth control pills contain synthetic hormones which are nearly equivalent to progesterone and/or estrogen. Even small doses of birth control pills suppress pituitary function (LH and FSH) down to very low levels (6). When dosing birth control pills Doctors never look at your FSH or LH or even your estrogen/progesterone levels.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy – Testosterone replacement therapy (especially in men) causes suppression of LH from the pituitary (7). But we don’t base dosing on the degree of LH suppression, instead we look at the level of testosterone and base dosing on that.
- Cortisol/Steroid use – Doctors will often use massive doses of “steroids” to reduce inflammation in autoimmune diseases. These massive doses suppress ACTH (the pituitary cortisol stimulating hormone) (8). Doctors do not check ACTH or even serum cortisol levels when using these medications even though long-term use of steroids has been shown to have serious detrimental side effects.
The TSH still has value and still should be checked in patients, but it may not be the single best marker to assess thyroid function in your body.
How Integrative Doctors Look at Thyroid Treatment
So now that you understand how conventional Doctors (endocrinologists and primary care physicians) look at thyroid management we can compare that to how more integrative doctors evaluate patients with thyroid disease.
And by integrative doctors, I am referring to doctors that may have extra training (outside of residency) in anti-aging medicine, integrative medicine or functional medicine.
The problem with this type of training is that it is not “standardized” which means that not all “integrative doctors” look at each patient the same.
Some doctors have used the term functional or integrative as a marketing tactic to simply get more patients even though they may not use a different approach from conventional physicians.
But in an ideal world, your doctor should be evaluating you in the following way:
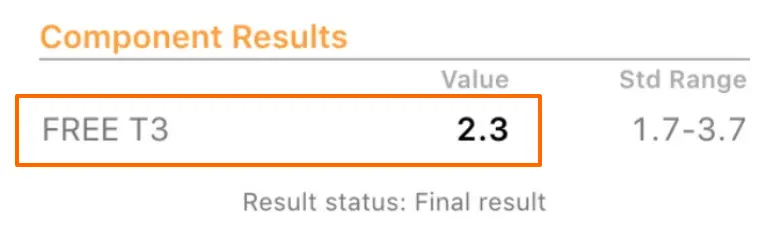
- Test for more than just the TSH – When evaluating your thyroid your free thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) give valuable insight as to how your body is absorbing and converting thyroid hormone. These free thyroid hormones (according to newer studies) track more closely with better outcomes when compared to other factors.
- Take into account individual genetics and preferences – Certain individuals are not able to convert or activate thyroid hormone at the same rate as others. SNPs in genes that control deiodinase enzymes can impact how you respond to T4-only thyroid medication (9). It is estimated that up to 15% of the population varies in their ability to convert T4 into the active T3 thyroid hormone.
- Take into account environmental factors such as stress, sleep, and diet – Lifestyle factors impact not only your thyroid but other hormones in your body as well! Your doctor should be treating you with more than just medications and supplements and should focus on the food that you put in your mouth and how you manage your stress. If they don’t address or ask about these questions then it may be time to seek a second opinion.
- Use more than just T4-only thyroid medications – In terms of thyroid medications, there is much more than just Synthroid and Levothyroxine. Other medications include NDT and T3/Cytomel/liothyronine. These thyroid hormones can be safe and incredibly effective if used appropriately.
As a patient, which approach would you rather have?
The rigid approach of conventional medicine is algorithmic, and the more individualized/integrative approach which is fluid and dynamic.
So What are you Supposed to Do?
So what are you supposed to do if you feel terrible and your Doctor isn’t willing to work with you?
Learning and reading are steps in the right direction, but it’s not a substitute for a knowledgeable doctor who can guide you through the process.
Your best bet is to seek out a physician who can help you and one who takes this more integrative approach.
Unfortunately, these types of doctors can be very difficult to find and they often don’t take insurance.
In order for these doctors to obtain this type of knowledge they usually have to do extra work and training after residency.
This means that not all physicians are equal in their understanding of these concepts which means they can be difficult to find.
Before you ask, I don’t know any or have personal recommendations to give you, or I would do so happily!
Because physicians have to learn this on their own we don’t have a secret group where we all talk or discuss patients.
Conclusion
If you are struggling with your current thyroid management then it may be time to seek out a second opinion.
Patients who have gone this route often report an increase in quality of life, an increase in energy, a reduction in weight, and many other benefits.
Don’t waste the best years of your life with physicians who don’t take your complaints and symptoms seriously!
Life is too short and your health is too important.
Now I want to hear from you:
Are you struggling with the current conventional approach?
Do you have questions about the integrative approach?
Which has worked for you? Which hasn’t?
Leave your comments below!