Reverse T3 could be the missing link to finally explain why you still have hypothyroid symptoms despite taking thyroid medication.
The crazy part is that most doctors don’t even order reverse T3 and, even if they do, most aren’t sure what to do with the results.
This means it’s up to you as a thyroid patient to understand what this lab test is, how to interpret your results, and how to manage high levels (if present).
High reverse T3 has the potential to slow down your metabolism, reduce thyroid function at the cellular level, and result in full-blown symptoms of hypothyroidism.
It may seem like a daunting task to learn all of this information but don’t worry, it’s not as hard as you think, and learning about it now can pay dividends to your future self.
Today you are going to learn…
- How to tell if you have too much reverse T3 in your body
- The name of the blood tests you need to have ordered
- How to calculate your free t3:reverse T3 ratio (and why this is important)
- What causes elevated reverse T3
- And how to “flush” out or lower high levels of reverse T3 and how I treat patients with Thyroid resistance and high levels of reverse T3 in my office
Let’s jump in.
What is Reverse T3 Anyway?
What it boils down to is this:
Reverse T3 is a hormone metabolite that is created from the T4 thyroid hormone (1).
T4 thyroid hormone, of course, is the primary thyroid hormone that your body produces directly from the thyroid gland.
Your body then takes T4 thyroid hormone and eventually breaks it down into T3, T2, T1, and sometimes reverse T3 through something called thyroid conversion.
A simplified version of that conversion process can be seen below:
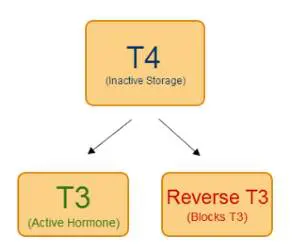
This conversion process is incredibly important to the body because it allows fine-tuning of thyroid hormone function throughout all of your cells.
And this is something you definitely want to happen, at least when it’s working correctly.
When it isn’t working correctly, the conversion process can slide down the wrong path which leaves you with the wrong types of thyroid hormone metabolites, namely reverse T3.
Unlike T4, T3, T2, and T1, which all have pro-thyroid effects, reverse T3 can be thought of as an anti-thyroid metabolite.
While T4, T3, T2, and T1 promote thyroid function, reverse T3 antagonizes thyroid function at the cellular level.
For people without thyroid disease, this conversion process works perfectly.
But if you have thyroid disease, especially for those taking thyroid medications, you can inadvertently alter this conversion process and lead to the creation of anti-thyroid metabolites which can act to make your thyroid function less efficiently.
Easy so far, right?
DOWNLOAD FREE RESOURCES
Foods to Avoid if you Have Thyroid Problems:
I’ve found that these 10 foods cause the most problems for thyroid patients. Learn which foods you should avoid if you have thyroid disease of any type.
The Complete List of Thyroid Lab tests:
The list includes optimal ranges, normal ranges, and the complete list of tests you need to diagnose and manage thyroid disease correctly!
Why Does Your Body Even Have Reverse T3?
That’s a great question and answering it will help you understand why, in certain situations, your body creates it.
The fact is we aren’t 100% sure why reverse T3 exists in the body but we can make some general assumptions about why it exists.
The prevailing thought, and one that I am in agreement with, is that reverse T3 is meant to act as a brake on your metabolism (2) during times of extreme stress.
Let’s look at chronic illness as an example:
When your body is recovering from an illness (like pneumonia or a bloodstream infection) does it make sense for your body to increase its metabolism and provide energy to your muscles?
Of course not!
It makes far more sense to conserve your energy and metabolism by slowing down energy production and providing energy to vital organs and your immune system to take care of the immediate threat.
This is a protective mechanism designed by the body to ensure that it can weather illnesses.
What may surprise you is that it has a name and is well-documented in medicine.
It’s known as euthyroid sick syndrome.

Patients who are under stress develop this condition by altering thyroid hormone metabolism through the conversion process I mentioned above.
Stress results in a typical change in thyroid lab tests manifested as low free T3, high reverse T3, and normal T4 and TSH levels.
I want you to take another glance at those lab tests mentioned above and even compare them to your results.
Do you see any similarities between your lab tests and the lab pattern typically seen in euthyroid sick syndrome?
If you are like many thyroid patients reading this then there’s a good chance you do.
But how can this be? Wouldn’t your doctor notice it?
You would think so but that isn’t the case!
Even though every doctor should have learned about euthyroid sick syndrome in medical school they believe that it’s a condition that only exists in extremely sick patients seen in the hospital or ICU.
Unfortunately, we are seeing more and more patients with multiple chronic medical conditions present with the same thyroid lab tests as those who are hospitalized which leads me to one important conclusion:
Maybe doctors are missing something about our current lifestyle, the increasing rates of illness and chronic medical conditions, and the impact that these have on reverse T3 and thyroid lab tests.
There are studies like this one (3) which can shed light on this very issue.
They show that other situations aside from being hospitalized can lower free T3 levels, increase reverse T3 levels, and cause changes in thyroid function that resemble “sick euthyroid syndrome“.
And it’s small things like this that may explain why so many thyroid patients walk around with hypothyroid symptoms despite being told they are “normal”.
Are You Pooling Reverse T3? High Reverse T3 Explained
Now that you better understand why you want reverse T3 levels to be as low as possible the next thing you need to understand is what causes them to be elevated.
Before we jump into the causes, though, let’s briefly go through some of the symptoms associated with an elevated reverse T3.
As you might suspect, the higher your reverse T3 the more hypothyroid you will feel.
Patients with high levels of reverse T3 tend to have one or more of the following symptoms:
- Decreased metabolism
- Lower than normal body temperature
- Cold intolerance
- Weight gain without changing eating habits
- Fatigue or low-energy
- Pain in the joints, muscles, or tendons
- Depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder
- Other symptoms of hypothyroidism
These are the most common symptoms but realize that each person will present in a different way from the next.
For instance, I’ve seen people with high levels of reverse T3 present with a complete inability to lose weight and with severe depression without manifesting the other symptoms mentioned.
Others may experience issues primarily with their body temperature and even others still may have a mix of all of those symptoms.
There’s obviously a significant overlap between the symptoms I mentioned above and other medical conditions which is why reverse T3 testing is very important (we will discuss this topic soon).
But first:
What causes elevated reverse T3 levels, and what should you look out for?
- Calorie-restricted dieting – Especially HCG-based diets or VLCD (very low-calorie diets). These diets (4) have been shown to reduce metabolism and increase reverse T3.
- Chronic illness and infections – This includes viral infections like infectious mononucleosis (5), bacterial overgrowth syndromes like SIBO, and even chronic illnesses like cancer, cardiac/heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and even obesity.
- Chronic Inflammation – Any cause of inflammation can result in decreased T4 to T3 conversion (6) and higher levels of reverse T3.
- Chronic untreated Gut infections – Up to 20% of T4 (7) is converted to T3 in the gut, which means if you have gut issues you may be missing out on up to 1/5th of your conversion power. Gut imbalances that thyroid patients deal with include SIBO, dysbiosis, reflux/GERD, yeast overgrowth, history of chronic antibiotic use, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Emotional and physiological stressors (8) – This includes social issues like the death of a loved one, family problems, divorce, etc. It also includes psychological (PTSD) and physical trauma (motor vehicle accidents, TBI, or otherwise) (8).
- Some Prescription Medications – The most common medications causing elevated reverse T3 include blood pressure medications, diabetic medications, anti-seizure medications, narcotics, and antidepressants. A common example is the use of beta blockers which can be used to treat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism (9) in addition to elevated blood pressure (10).
What You Need to Know About Reverse T3 Testing
Reverse T3 testing is actually pretty straightforward.
There is a serum marker for reverse T3 that most standard lab companies can run.
What isn’t always straightforward is interpreting your results, but even that is not as difficult as it may sound.
Before we talk about interpreting your results, it’s important to understand how reverse T3 testing fits into a complete thyroid lab panel.
There are no fewer than 4 standard lab tests that need to be run to adequately assess thyroid function and each of these lab tests provides you with different information.
You never want to just order one lab test without the others because you won’t get the information you are looking for.
This applies to reverse T3 just as much as it applies to TSH testing.
This means if you are planning to really understand your thyroid, you will need to get the following thyroid lab tests: TSH, free T3, free T4, reverse T3, and thyroid antibody levels.
Obtaining these other lab tests will help you put your reverse T3 level into context, especially when combined with your symptoms.
One of the most powerful use cases for reverse T3 is in catching early thyroid disease.
Take a look at this image to see what I mean:
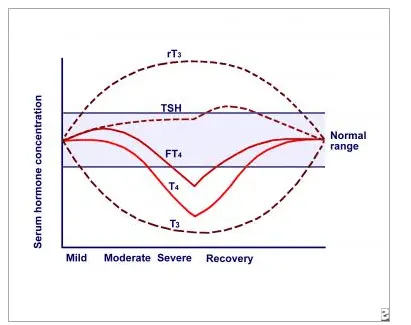
This image demonstrates the severity of the disease state on the X-axis and the concentration of thyroid hormones on the Y-axis.
Basically, it shows what happens to thyroid lab tests and when they become abnormal in relation to the severity of your disease.
What should stand out to you is the fact that reverse T3 (abbreviated as rT3) and T3 (abbreviated as T3) are the earliest markers of thyroid dysfunction.
They become abnormal much sooner than the other thyroid lab tests which makes these lab tests sensitive for diagnosing early thyroid problems.
What’s more, is that the difference between these two lab tests is more dramatic and pronounced than any other thyroid lab test.
For this reason, these two lab tests are critical in evaluating thyroid function.
You can determine the spread between these two values with a simple calculation which will give you the ratio of reverse T3 to free T3.
This ratio is called the free T3:reverse T3 ratio and is something that every thyroid patient should calculate using their own thyroid lab tests.
In an ideal world, you want your free T3 levels to be as high as possible (generally upper 1/2 to 1/3 of the “normal” reference range) and you want your reverse T3 levels to be as low as possible.
To calculate your free T3: reverse T3 ratio simply divide the numbers.
Your ratio should be > 0.20.
Any ratio < 0.20 indicates too much reverse T3 to free T3 and means that you should focus on either increasing your free T3 or reducing your reverse T3.
In order for this calculation to work, your units must be the same.
The units used in the United States for free T3 are pg/mL and the units used for reverse T3 are ng/dL.


Using the example above, if you divide 2.8 by 14.4 you are given a value of 0.19 which is less than that <0.20 level mentioned above.
If your free T3 and reverse T3 lab tests are not in these units, you can easily convert them and then make the calculation with some simple tools available online.
If you want a down-and-dirty way to assess your reverse T3 then you can also just look at the absolute value.
In most patients, a reverse T3 level of less than 15 ng/dL is ideal.
Values higher than this tend to start causing problems, especially if associated with a low free T3.
How to “Flush” Out Or Lower Reverse T3 Levels
So you’ve found out that your reverse T3 level is elevated, what now?
Your next step should be to try and drive that level as low as possible.
This is sometimes referred to as lowering reverse T3, treating reverse T3 pooling, or flushing reverse T3 out of your system.
These are all different names used to describe the treatment of high reverse T3.
What I want you to be aware of is that treatment should focus on
What you need to be aware of is that the treatment will focus primarily on the underlying cause (11).
Because of this, there really isn’t a one-size-fits-all treatment program that I can recommend.
I can and will give you recommendations for common causes, but you will still need to tailor that to your specific situation.
With this in mind, let’s talk about 5 different ways that you can lower reverse T3:
#1. T3 Containing Thyroid Medications
The fastest and easiest way to get rid of excess reverse T3 is with bioidentical hormone formulations that contain pure T3 thyroid hormone.
This would include medications like liothyronine, Cytomel, or sustained-release T3.
The reason this approach works so well is that when you give your body T3 hormone directly it automatically suppresses T4, which reduces the substrate that your body uses to create reverse T3.

In essence, you’re starving out the ‘food’ source your body uses to make reverse T3.
Naturally what will happen with T3 medication use is that your T4 levels will decrease, your free T3 levels will increase, and your TSH will decrease.
While on T3 thyroid medication it’s important to monitor reverse T3 closely, at least once every 6 to 8 weeks.
Typically within 2 months (and assuming your dose of T3 is high enough), your reverse T3 should drop to less than 10.0.
This is definitely the fastest way to reverse T3, but it doesn’t take into account the underlying cause.
So if you use T3 to reduce your reverse T3 without making any other changes, it’s likely that your reverse T3 will just jump back up once you stop taking T3 medication.
Is NDT Helpful for Reducing Reverse T3?
It certainly can help but there are a few things to realize if you want to use this class of medications to treat reverse T3:
- Each grain of NDT has about 38 mcg of T4 and 9 mcg of T3, which means that NDT still primarily consists of T4.
- In order to flush out the reverse T3, you must lower the substrate of T4 which generally means lowering your total dose of T4. In some cases, you may have to drop your NDT dose in favor of pure T3 medications.
- NDT dosing is static meaning you can’t individually alter the concentration of T4 and T3 unless you add additional thyroid medications.
You can still treat elevated reverse T3 with the use of Natural Desiccated Thyroid, but it’s generally not considered the best option.
#2. Supplements Can Enhance T4 to T3 Conversion
In addition to medications, every thyroid patient should also consider utilizing nutritional supplements.
The reason is simple:
The hypothyroid state sets the body up for certain nutrient deficiencies and since most thyroid patients are under-treated, most also have these deficiencies.
This is for 2 main reasons:
The first is that low thyroid states lead to low stomach acid which leads to decreased absorption of nutrients across the board.
The second is that low thyroid states also increase your risk of developing gastrointestinal imbalances which may further impair the absorption of minerals and nutrients.
You can check out this post here for more info about which supplements you should consider using and how to check to see what your body needs.

If you are trying to support the conversion of T4 to T3 with the use of supplements then there are a few you should pay special attention to.
The two primary supplements that you should focus on are zinc and selenium. Both of these supplements have been shown in some clinical studies (12) to increase T4 to T3 conversion, thereby potentially decreasing reverse T3.
In addition to zinc and selenium, I’ve also seen great success with guggulsterone or guggul extract.
We aren’t as concerned about supplements that promote thyroid hormone production (such as iodine and L-tyrosine), but they can still be helpful in some cases.
In addition to these supplements, you can also check out some natural therapies that have some good data behind their use as effective tools for naturally improving T3 levels and reducing reverse T3 levels.
#3. Reversing Hormones that promote T4 to Reverse T3 Conversion
As you are probably aware your hormones all work in tandem with one another.
This means that as one system slows down it may drag down other systems or cause an increase in other hormones to make up for the deficit.
This relationship holds true for thyroid hormones and their impact on leptin and insulin levels.
The link between these hormones is clear:
This is very important because hypothyroidism leads to a state where developing both insulin and leptin resistance becomes much easier.
Why do we care?
Because insulin and leptin resistance both cause inflammatory states which contribute to T4 to reverse T3 conversion.
Not only do they contribute to high reverse T3 levels but they also make weight loss very difficult.
Patients with high reverse T3 levels almost always have high fasting insulin and high fasting leptin levels.
In fact, I don’t think I have ever seen a patient with a reverse T3 greater than 25 with a normal insulin or leptin level.

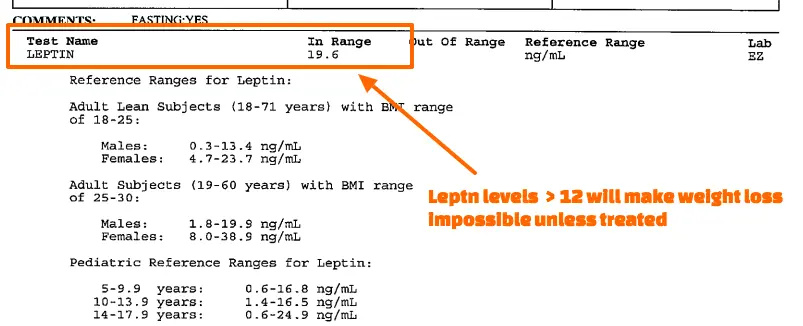

You can see examples from several patients above showing abnormal reverse T3 levels, high fasting leptin, and high fasting insulin levels.
These values may fall within the “normal” range but they are far from normal and will lead to symptoms of hypothyroidism, weight gain, and weight loss resistance.
Another big reason I want to talk about these hormone imbalances is that doctors don’t frequently run tests to check for either of them.
Doctors will routinely check hemoglobin A1c but rarely order fasting insulin and fasting leptin levels.
This means that if you have known thyroid conversion problems, it’s probably going to be up to you to request these additional hormone tests.
Treating and reversing both insulin and leptin resistance is very important for not only lowering reverse T3 but maintaining low levels over time.
To learn more about how to address these hormone imbalances please see the following case studies below:
- Victoza weight loss: 40 pounds lost with Victoza + LDN
- Byetta weight loss: 42 pounds lost over 3 months
- Hashimoto’s weight loss: 55+ pounds lost over 9 months with before/after pictures
These case studies provide a step-by-step walkthrough of how to approach leptin and insulin resistance including which medications, hormones, and supplements are most effective.
If you know you have insulin resistance then you can consider using these supplements to help lower your levels:
- Berberine: Helps reduce cholesterol, improve fasting glucose, and may help with weight loss.
- Alpha Lipoic acid: Helps sensitize the body to insulin and may help to reduce nerve damage in certain patients
- Chromium: Helps improve insulin sensitivity to cells and may help reduce cardiovascular disease in certain patients.
If you prefer the natural approach to treating leptin levels you can find more information here.
#4. Addressing Inflammatory Levels and “Cooling Off” Your Body
Everyone knows inflammation is bad for the body (15), but very few people understand how it makes things worse and, more importantly, how to address it.
Part of the reason for this is that the markers we use for inflammation are non-specific.
That means most of the time we know inflammation is present, we just don’t necessarily know what’s causing it.
Sure, in the presence of other abnormalities we might be able to take a guess, but we will rarely ever know with 100% certainty.
And this is a problem because inflammation is a known contributor to thyroid conversion problems.
We know that inflammation directly promotes the production of reverse T3 (16) by pushing your body down the T4 to reverse T3 conversion pathway.
So if you have high reverse T3 levels you need to be actively searching for sources of inflammation and treating the underlying cause.
You can easily test for inflammation by ordering these lab tests:
- CRP: You want this to be as low as possible but definitely < 1.0 for optimal thyroid function.
- ESR: Another non-specific marker of inflammation (17), for optimal thyroid function this should be < 10.
- Ferritin: Both a marker for iron stores and an acute phase reactant (18), this marker can be used in certain instances to help isolate non-specific inflammation in the body.
If you know that you have both high levels of inflammation and high levels of reverse T3 then you can safely assume that the inflammation is likely worsening your thyroid function.
The next step is to find where it’s coming from.
In hypothyroid patients it’s usually in these three places:
- Hormone imbalances (especially insulin and leptin resistance)- Please refer to the section above to understand how to both diagnose and treat these conditions.
- Undiagnosed gut imbalances like SIBO and SIFO – Both of these gut issues promote inflammation (19) in the GI tract and lead to increased intestinal permeability. You can find more about both here.
- Undiagnosed food sensitivities – These sensitivities promote inflammation (20) and further food sensitivities unless treated.
Bottom line?
If you have both high reverse T3 and elevated serum markers for inflammation you should be looking at the 3 main causes above and treating those if applicable.
If you don’t know where the inflammation is coming from you can still do some good by taking supplements designed to help reduce inflammatory levels and promote the “clean up” of breakdown products in the liver:
- Milk thistle + MSM: Designed to help improve liver function and promote proper phase 1 and phase 2 elimination of medications, supplements, and other products that need elimination in the liver. This combination may also help reduce AST and ALT levels (21)(if you have fatty liver).
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids: Omega 3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation by reducing inflammatory cytokines.
- Curcumin: This well-studied herb activates PPAR-gamma levels (22) helping to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Quercetin & Bromelain: Particularly helpful in patients with digestive issues and those with chronic sinus/upper respiratory illness-like symptoms (post nasal drip and chronic stuffy nose).
This approach isn’t ideal but it’s better than simply ignoring it.
#5. Lifestyle changes to Balance Hormones and Promote Thyroid Function
Never underestimate the power of these 4 major areas when it comes to improving your thyroid:
- Getting 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night
- Reducing and managing your stress
- Daily low-intensity exercise and episodes of high-intensity exercise 1-3x per week
- A well-balanced diet full of real, whole foods
If you don’t practice these 4 basic things it doesn’t matter what you do, you won’t get better.
These are particularly important for those with high reverse T3 levels.
Remember that your body is a network of systems and hormones that all interact with one another.
When one system isn’t working properly, it will bring other systems down.
These areas are so important that many thyroid patients can see significant improvement in their thyroid symptoms by optimizing them without the need for additional treatments or medications.
The only problem is that most thyroid patients take them for granted and would prefer to take a supplement and call it a day.
Don’t fall into this trap!
Take that supplement if you want, but make sure you are also paying attention to your diet, exercise routine, sleep schedule, and stress levels.
Final Thoughts
Elevated reverse T3 is a serious issue for many thyroid patients and it’s a problem that is often ignored by many conventional doctors and endocrinologists.
The best way to evaluate your reverse T3 is by testing for it along with free T3 and free T4 levels.
To get a better idea of how reverse T3 is impacting your body, you can measure your free T3:reverse T3 ratio.
If your free T3/reverse T3 ratio is < 0.2 you have too much reverse T3 in your body.
The fastest most effective method for optimizing reverse T3 is with the use of pure T3 thyroid medication.
Now I want to hear from you:
Is this the first time you’ve heard about reverse T3?
Have you had your levels checked? If so, was it high or low?
What type of treatments have you tried to lower your reverse T3?
Have you tried medications that contain T3 like Cytomel or liothyronine? Did they work for you?
Leave your questions or comments below!
Scientific References
#1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3428867
#2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7355063
#3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12055988
#4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12055988
#5. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/infectiousmononucleosis.html
#6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11716958
#7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3049061
#8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28/
#9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3475282/
#10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5369873/
#11. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399020
#12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8157857
#13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3608008/
#14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3356957/
#15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3492709/
#16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3978663/
#17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4653962/
#18. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24549403
#19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3099351/
#20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1774228/
#21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17548789
#22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2234255/