Dysregulation of estrogen levels is incredibly common among women.
High and low estrogen levels contribute to conditions such as low sex drive, weight gain, PMS/PMDD, depression, mood changes, and even other hormonal problems.
The good news is that there are targeted supplements that you can take to influence and manage your estrogen levels.
Use this guide to help determine if you have low estrogen or high estrogen and what kind of estrogen supplements may help you and your symptoms:
Why You Need Normal Estrogen and Sex Hormone Levels
All sex hormones are important for women, but estrogen may be at the top of that list.
While women tend to have more testosterone and progesterone (in absolute values) in the body, it is really the balance of these hormones that matters most.
High (or low) estrogen tips the balance and promotes the symptoms that people associate with various issues.
For instance:
High estrogen levels (relative to progesterone) can lead to symptoms such as PMS, PMDD, menstrual irregularities, fibrocystic breast disease, breast cancer, etc.
On the other hand, low estrogen can lead to various symptoms such as vasomotor issues (hot flashes), weight gain, increased risk for bone loss (1), and even an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (2).
Hopefully, this makes clear the point that you NEED estrogen in the body for proper function, but you also don’t want too much or little at all.
It’s helpful to think of estrogen and progesterone as polar opposites to one another.
While estrogen helps build up tissues and glands, progesterone is needed to balance that effect to make sure it doesn’t go out of control.
This also helps explain why the female body goes through hormonal cycles throughout the month where each hormone is higher for a short period of time.
This balance must be maintained to help the proper growth of the female body and changes to this system can result in dramatic changes overall.
You can think of estrogen as a “growth hormone” in your body…
Meaning that it helps build up endometrial, breast (3), and even fat tissues.
This explains why many women with higher than normal estrogen levels tend to develop weight gain – predominately in the hips/thighs/glut region.
Progesterone, on the other hand, helps balance this effect and can reduce growth in these tissues (yes, it can even help with fat loss!).
This insight can help us understand how to treat estrogen-related issues, knowing that hormones MUST be in balance with one another.
Often treatment needs to be focused on both estrogen and progesterone in order to maintain balance.
If you are having issues with your estrogen you will know it because you will have symptoms.
Below I am going to go over what causes changes in estrogen levels and what symptoms tend to be associated with these various changes in estrogen levels.
Once we know what the problem is we can talk about how to address these estrogen levels with various supplements and treatments…
- Bottom line: Estrogen and progesterone must be maintained in balance with one another. Changes to either can tip the balance and result in symptoms and dysregulation of the estrogen/progesterone ratio.
What Causes High Estrogen
Having too much estrogen is probably more common than having too little estrogen (at least for pre-menopausal women).
High estrogen levels are quite common in many patients simply due to the biochemistry of the body.
As women gain weight several factors occur that lead to high estrogen:
1. Weight gain contributes to insulin resistance which causes further weight gain.
2. Insulin resistance causes high androgens and high testosterone (leading to PCOS-like syndromes).
3. High levels of testosterone can be converted into estrogens through aromatization.
4. Weight gain reduces thyroid function leading to reduced circulating thyroid hormone contributing to low progesterone and thus higher estrogen levels.
This process occurs as a result of weight gain, but these steps can happen whether you are overweight or not.
As a result, many women have a higher than normal estrogen level and a condition known as estrogen dominance (meaning higher than normal estrogen levels compared to progesterone levels).
Aside from these very common hormonal changes, other factors can increase estrogen levels like the standard American diet, a diet high in soy-based foods, exposure to chemical xenoestrogens, and even high levels of stress.
This constellation of conditions and syndromes usually occurs in pre-menopausal women (meaning women who are in their 20-40’s), but even menopausal women can have more estrogen than they need due to excess weight gain.
Excess weight after menopause can act as a reservoir for estrone production through the fat cells.
So women can end up with higher than normal estrogen levels before and after menopause.
Causes of high estrogen levels in women:
- Insulin resistance & high blood sugar (4)
- Hypothyroidism/Hashimoto’s (5) (thyroid hormones have direct effects on thyroid follicular cells, alterations in thyroid hormone alter sex hormones including progesterone)
- Weight gain & Obesity (6) (androgens can be turned into estrogens through aromatization in adipose/fat cells)
- High cortisol levels & Hypercortisolism (7)
- High-stress levels (8)
- Poor Diet (9) (including a diet high in soy)
- Xenoestrogens (10) due to chemicals and environmental exposure
Symptoms of High Estrogen or having too much estrogen relative to progesterone
While estrogen levels can change dramatically in women due to their cycle (making diagnosis difficult) there are several symptoms that tend to accompany this dysregulation of estrogen/progesterone.
If you aren’t sure if you have high levels of estrogen use the list below to help guide you.
Having this information will also help to determine which treatment and supplements you should use to balance your estrogen.
- Breast tenderness
- Breast fullness
- Malaise or fatigue
- Depression or anxiety
- Abnormal bowel movements
- Bloating
- Water retention especially swelling in the fingers or legs
- Increased irritability or impatient but with a clear mind
- Nipple tenderness
- Pelvic cramps
- Hot flashes (if VERY high)
- Symptoms of PMS/PMDD
- More prolonged exposure may lead to fibrocystic breast disease, uterine/endometrial growth
While these tend to be the most common symptoms of high estrogen levels each patient may react differently.
These symptoms result from excess estrogens (including estradiol, estrone, and estriol) relative to progesterone levels.
That means having low progesterone with normal estrogen levels may also contribute to and cause these symptoms.
Look to your ratio, not the absolute number of your estrogen when evaluating these hormones.
What causes Low Estrogen
High estrogen is much more common in pre-menopausal women while lower estrogen levels are more common post-menopause.
All women will eventually develop low estrogen levels when compared to menstruating women.
The decline of estrogen largely depends on other factors including how much metabolic damage is present prior to menopause, what other hormone imbalances these women have, and how much weight they have going into menopause.
While high estrogen is more common than low estrogen levels, it’s still very important to understand and diagnose.
Because all women will eventually go through menopause it’s still very important to talk about how to treat low estrogen levels.
Causes of low estrogen:
- Menopause
- Hysterectomy(chemical or surgical)
- Extreme dieting, extreme weight loss, or extreme metabolic damage(usually a result of starvation-type diets or eating disorders)
- Extreme stress(prolonged and constant)
- Pituitary failure
- Extreme exercise
Symptoms of low estrogen
Estrogen is felt to have inhibitory effects on body weight through various mechanisms.
Estradiol helps maintain control over fat-regulating hormones (11) like insulin and leptin.
When estradiol levels fall after menopause these systems tend to favor higher levels of both insulin and leptin.
If you’ve read my blog before you know that both leptin resistance and insulin resistance contribute significantly to weight gain.
This may explain, at least in part, why postmenopausal women tend to gain at least 10+ pounds at the onset of menopause (12).
In the case of leptin, estradiol actually helps sensitize the brain to this hormone which helps to increase its effectiveness.
When your body is sensitive to leptin your metabolism will remain normal and regulated.
Once this sensitization decreases, as a result of menopause or hysterectomy, the brain becomes more resistant to leptin which results in weight gain and weight loss resistance (13).
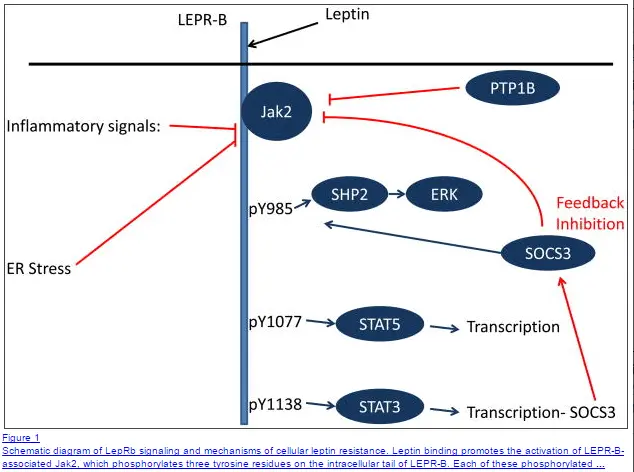
Estradiol also helps to reduce food intake (appetite) by modulating serotonin levels in the brain (14).
This may explain why women get food cravings throughout their cycle and during pregnancy!
Normal estradiol levels help you know when you should stop eating and actually helps reduce overeating (AKA hyperphagia).
The importance here is that once estrogen levels fall (either from menopause or hysterectomy) your appetite loses some of that regulation through serotonin.
This change may result in increased cravings for foods that may lead to weight gain long term.
These certainly aren’t the only symptoms of low estrogen levels (there are many more that we will go over below), but weight gain tends to be one of the most concerning symptoms of low estrogen.
Symptoms of low estrogen:
- Warm rushes
- Hot flashes
- Night Sweats
- Temperature swings
- Sleep disturbance & insomnia
- Racing mind especially at night
- Mental fogginess or forgetfulness
- Dry vagina, dry eyes & dry skin
- Pain during intercourse
- Loss of “glow” to the skin
- Diminished sensuality and sexuality
- Episodes of heart palpitations or rapid heartbeat
- Fatigue, low energy, or reduced stamina
- Headaches and/or migraines
- Weight gain in the thighs/hips or buttocks region
- Intestinal bloating
- Back and joint pain
Use the list of symptoms above to help guide you to determine which type of estrogen problem you may be suffering from.
Then you can match your symptoms to the treatment outlined below.
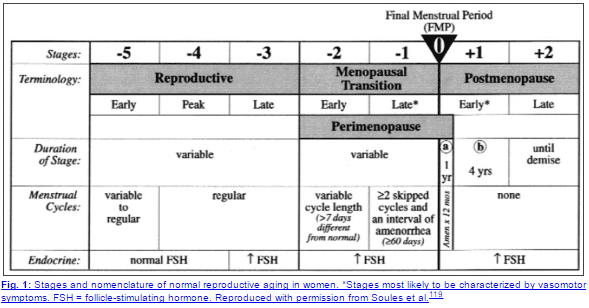
It’s also important to note that some women can have higher than normal estrogen levels even after menopause.
This has to do with the fact that women can still create some estrogen through androgens (aromatization), while progesterone levels are almost always zero in postmenopausal women.

You can see this concept illustrated above, where progesterone levels drop and stay very low compared to estrogen levels through pre-menopause and post-menopause.
The more fat you have in your body, the more estrogen you will produce even after ovarian failure.
Remember it is the ratio of progesterone to estrogen that is most important and determines how your body will react.
Supplements to help Lower and Balance High Estrogen Levels
We will start discussing how to help balance estrogen levels if you know you already have higher levels.
Most women will fall into this category as a result of weight gain, hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, etc.
These conditions are far more common nowadays and represent the majority of younger females.
There are 3 strategies that we can employ to help balance and lower estrogen levels in women:
First:
Help the body metabolize and get rid of estrogen.
Estrogen actually has complex metabolism in the body and in the liver.
Estradiol is broken down into other smaller estrogen products that have estrogenic properties and can sit on and activate estrogen receptors in the body (in some cases these estrogen breakdown products can actually reduce the risk of breast cancer (15)).
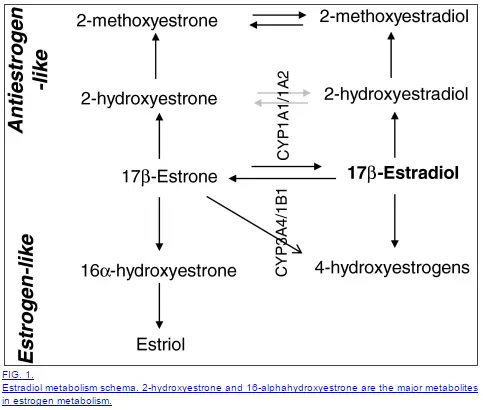
This makes the elimination of excess estrogen very important and it’s something that we can directly impact.
Second:
Help reduce the impact that other hormone imbalances have on estrogen levels.
As we mentioned before other hormones either directly or indirectly impact estrogen levels.
One of the most obvious targets is testosterone and other androgens.
These androgens can directly turn into estrogenic compounds through fat cells.
By reducing this conversion process (and by reducing fat cells) we can effectively help to lower estrogen levels throughout the body.
Third:
Indirectly help estrogen levels by directly increasing progesterone levels.
By directly taking progesterone you can counteract some of the high levels of estrogen.
By itself, this isn’t the best option, but it can absolutely be very helpful if combined with the other therapies listed above and in women who have very low progesterone levels.
To get the best results, make sure you employ multiple therapies listed below. Doing just 1 or 2 of these will not result in dramatic results.
#1. DIM & Indole 3 Carbinol
DIM stands for Diindolylmethane which is a bioactive compound derived from cruciferous vegetables.
Indole 3 carbinol is an earlier breakdown product of DIM but both have been shown to help your body naturally metabolize and get rid of estrogen levels.
Studies have shown (16) that DIM and indole 3 carbinol can help the body eliminate estrogen levels and even promote the healthier estrogen breakdown products of 2-hydroxy estrone and 2-methoxy estrone.
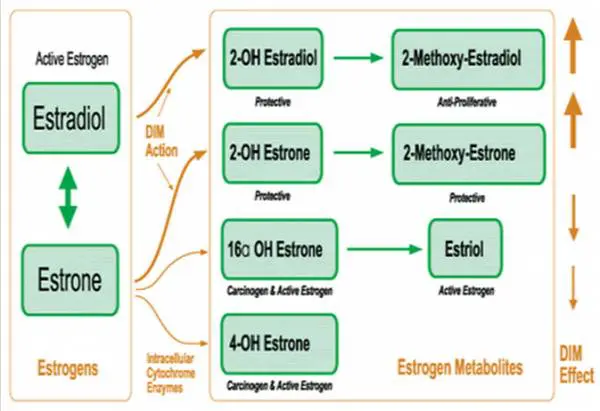
By encouraging this metabolism your body can get rid of estradiol faster and more efficiently.
How to Supplement with DIM & Indole 3 carbinol
- Take 100 to 300mg per day of this supplement
- You may benefit from taking more DIM right before ovulation and toward the end of your cycle when estrogen levels are highest
- Monitor your symptoms while taking DIM to ensure that you tolerate the supplement
- Take this supplement in addition to consuming more cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and bok choy
#2. Zinc & Saw palmetto
Zinc and saw palmetto act through a backdoor mechanism to help reduce estrogen levels.
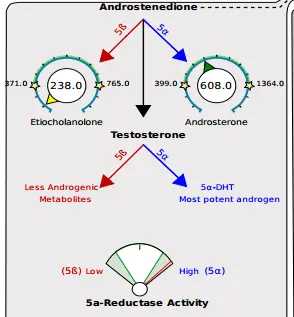
As I mentioned previously you can get high estrogen levels from high levels of testosterone and DHEA.
These androgens can be metabolized into estrogens in fat cells, so having high testosterone and/or lots of fat will both indirectly lead to high estrogen.
Zinc and saw palmetto act by helping increase the metabolism of testosterone and help the body eliminate the testosterone.
An added benefit of zinc and saw palmetto is that they also act to help reduce the symptoms of high testosterone such as hair loss, acne, low energy, and weight gain.
Zinc and saw palmetto both act by reducing the activity of the enzyme 5 alpha-reductase (17) which turns testosterone into the potent androgen (5x more potent than testosterone) Dihydrotestosterone.
Instead of going down the 5a pathway, zinc and saw palmetto help the body prefer the 5B pathway to create less androgenic metabolites.
How to Supplement with Zinc & Saw palmetto
- Take up to 5-15mg per day of zinc – Zinc can also help promote proper thyroid function and immunity
- Take up to 600mg per day of Saw palmetto
- Combine both therapies for maximum benefit
#3. Calcium D-Glucarate
This supplement helps your body directly eliminate excess estrogens but it also helps with the proper metabolism of testosterone/androgens AND cortisol/glucocorticoids.
Calcium d-glucarate is a substance derived from glucaric acid which is found in fruits and vegetables.
It works by inhibiting an enzyme in the body known as beta-glucuronidase which is involved in the phase II liver detoxification pathway.
In a nutshell: higher levels of Glucaric acid and calcium d-glucarate help the body change the chemical structure (18) of pretty much everything your body comes into contact with to help your body eliminate it.
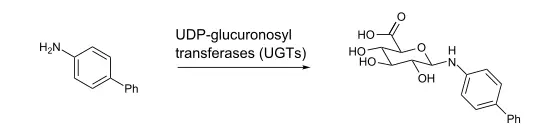
In order for your body to get rid of something very large (like a hormone) it has to be cut into smaller pieces, and your body does this primarily in the liver.
Glucuronidation is one of the ways that your body changes the structure of chemicals and “cuts” them into smaller pieces.
Unfortunately, the enzymes responsible for these reactions can be influenced (or slowed down) by medications, chemicals, hormones (including hypothyroidism), and age.
This specific pathway is responsible for the elimination of estrogens and other hormones.
So when this system gets “slowed” by various conditions, your body may accumulate more estrogen and/or estrogen metabolites.
Taking calcium d-glucarate has been shown to unblock the system (19) and help it function more efficiently by helping the body eliminate excess estrogen.
How to Supplement with Calcium d-glucarate
- Higher doses of calcium d-glucarate may be necessary for the best results. Start off by taking 500mg per day and slowly increase your dose up to 3,000mg per day.
- While increasing your dose monitor for negative side effects or “detox” like reactions: flu-like symptoms, muscle aches, acne, etc.
- Calcium d-glucarate helps the body eliminate more than just estrogen metabolites – this will also help your body eliminate medications, cortisol, testosterone/androgens, and bile acids (anything that is eliminated via glucuronidation)
- Calcium d-glucarate can also be used in short bursts to help eliminate medications, chemicals, etc. that you may have come into contact with and this method may be superior to taking it daily
#4. Maca Root
Maca is another supplement that has the potential to improve multiple conditions in both men and women.
While studies have shown that it has the potential to improve sexual behavior, fertility, mood, memory, osteoporosis, and even metabolism (20) – the exact mechanism is still not well understood.
Maca root seems to help by balancing issues with your sex hormones:
If your estrogen level is higher it tends to help lower it, if your testosterone is low it tends to help increase the effectiveness of what testosterone you do have.
Much of these effects likely occur at a cellular level because supplementation doesn’t appear to alter serum levels of sex hormones (21).
Having said that many people who supplement with maca report impressive results (22).
If you are having issues with estrogen AND other symptoms like low sex drive OR issues with low testosterone, then supplementation with maca would be a consideration.
Maca also has the added bonus of acting as an adaptogen which means it can improve energy levels and may balance cortisol levels.
How to Supplement with Maca root
- Start with 1 tablespoon of maca powder per day, and increase the dose up to 1 tablespoon 2-3x per day as tolerated
- Maca is generally well tolerated, most patients notice a difference when supplementing within 3-4 weeks
#5. Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogen that can help women with high estrogen in multiple ways:
First:
Ashwagandha appears to have some effect as an anti-estrogen compound.
Meaning that taking this supplement can help balance and reduce estrogen levels in the body.
It appears to do this by downregulating estrogen receptor alpha (23) (an estrogen receptor that turns “on” estrogen-related genes).
Second:
It helps to reduce symptoms of high estrogen-like weight gain, depression, and low energy.
Ashwagandha is another adaptogen which means that it has powerful effects on other systems in the body.
Supplementation with ashwagandha has been shown to increase libido (24) (low libido is usually a sign of sex hormone imbalance) and decrease symptoms of depression.
Third:
Lastly, ashwagandha can help to regulate cortisol levels.
Remember when we discussed how all hormones in your body are intertwined?
Well, high cortisol levels can certainly impact estrogen levels and ashwagandha helps to balance cortisol levels which indirectly alters estrogen.
Taking this adaptogenic herb has also been shown to increase energy levels and treat symptoms associated with low/high cortisol.
How to Supplement with Ashwagandha
- Dosage varies from 500-2,000 mg per day depending on tolerance and degree of symptoms
- Length of treatment varies by condition, for adrenal fatigue supplementation as long as 6+ months may be required.
Supplements to help Increase Estrogen and help Women in Menopause
While many women suffer from too much estrogen, there are still many women who suffer from not enough estrogen.
This usually occurs in patients post-menopause who start to see the signs of low estrogen in their bodies.
Increased aging of the skin, increased pain during intercourse, increased risk of urinary tract infection, and so on.
Many women even suffer from the more debilitating symptoms of having low estrogen such as insomnia, hot flashes, and depression that can really impact their quality of life.
Using these supplements can act as a buffer to help balance estrogen levels either directly or indirectly.
While these supplements may potentially help women with low estrogen, they will not necessarily work for everyone.
In some cases, women may benefit from the use of bio-identical estrogen compounding with both estradiol and estriol.
These supplements should act as a first-line therapy though due to their low-risk profiles and ease of use.
If, however, they do not work within 3-6 months it may be worth pursuing prescription options.
#1. Flaxseed
Flaxseed has been shown in multiple studies to help reduce the symptoms associated with menopause:
- Reduces mild symptoms of menopause including hot flashes and other vasomotor symptoms (25)
- Improves quality of life in menopausal women (26)
- Is superior to soy at balancing estrogen levels due to phytonutrients (27)
- Also lowers insulin and glucose levels and may assist with weight loss efforts in postmenopausal women (28)
Flaxseed does NOT appear to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, however, and that should be considered if you are at high risk or have a family history of heart disease.
How to Supplement with Flaxseed
- Start with 2-4 tablespoons of organic flax seed per day
- You can add this to your breakfast smoothies, sprinkle over your food or fresh fruit, add it to salads, etc.
- Flax is a source of healthy fats and omega fatty acids, don’t be afraid to use it due to the fat content
#2. Black Cohosh
Black cohosh is another supplement that has been shown in clinical studies to help reduce the symptoms and severity of menopause (29).
Black cohosh is felt to alter estrogen levels by acting as a selective estrogen receptor modulator.
It also appears to lower inflammation, act as an anti-inflammatory agent, and increase/balance serotonin levels (30).
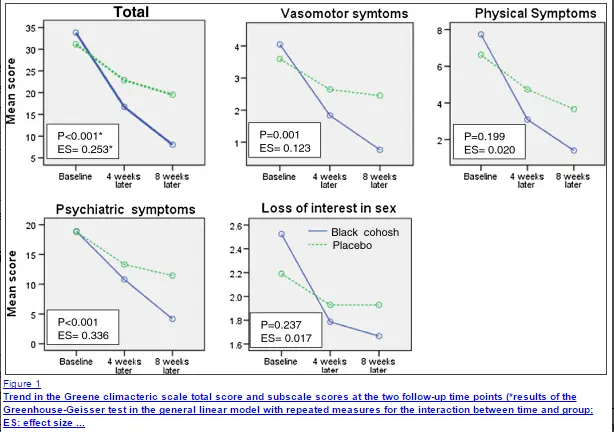
Through these effects patients taking black cohosh (who are also menopausal) have shown a reduction in hot flashes and other vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause.
Taking black cohosh during menopause has also been shown to be safe (31).
How to Supplement with Black Cohosh
- Start with 250mg per day (you may go up to 500mg depending on tolerance and your symptoms) – if you don’t have relief of your symptoms within 2-4 weeks then consider increasing your dose
- For best results, women in menopause should use it for 3-12 months
- Taking for this length of time has been shown to reduce menopausal vasomotor symptoms by up to 35%
#3. Evening Primrose Oil
Taking evening primrose oil has been shown in studies (32) to help reduce mild symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes.
These studies show that evening primrose oil actually helps reduce the severity and intensity of hot flashes.
In addition, women taking EPO were also noted to have a better quality of life while on this supplement.
How to Supplement with Evening Primrose Oil
- Start with 250mg per day
- Increase dose up to 1,000mg per day as tolerated
#4. Vitamin K2 +/- D3
Vitamin D3 and K2 are added here because they are very important for calcium regulation in the body.
While they won’t help with your estrogen levels directly they may help fight off or reduce your risk of developing calcium-related issues like bone loss which IS related to low estrogen levels.
Vitamin K2 should be taken with vitamin D3 (make sure it’s in the D3 form) because both are involved in calcium regulation in the body (33).
Vitamin K2 helps direct calcium stores to where they should be (in your bones) and away from places they shouldn’t be (like in your coronary arteries).
Having normal vitamin D levels is required for proper immunity, energy levels, and regular mood.
Most patients I test have low levels of vitamin D due to lack of sun exposure during optimal times of the day.
How to Supplement with Vitamin D3 + K2
- Use 2,000 to 5,000 IU of D3 per day, and make sure to follow your serum vitamin D levels
- Take these vitamins with a meal high in fat to help increase absorption
- Use up to 15mg per day of vitamin K2 liquid as necessary
- Most people take too much D3 and not enough vitamin K2
#5. DHEA
DHEA makes the list because it is an androgen that can actually help improve testosterone and estrogen levels indirectly.
DHEA is a precursor hormone in your body.
Your body uses DHEA to create estrogen AND testosterone metabolites.
DHEA, along with testosterone, tends to decrease as we age.
This indirectly results in reduced levels of testosterone and estrogen due to decreased conversion to these hormones.

You can supplement with DHEA to increase your reservoir of this hormone.
One of the downsides to supplementing with DHEA is that you don’t have control over what your body will do with it.
This means your body may take the DHEA and turn it into estrogen or it may go and turn it into testosterone (or an equal amount of both).
Most patients take it with one goal in mind, but it doesn’t always work out that way so keep that in the back of your mind if you choose to supplement with DHEA.
DHEA is available over the counter, but it is a powerful androgenic hormone so don’t let that confuse you into thinking that it is harmless.
How to Supplement with DHEA
- Start with 25mg used every 3 days
- If you tolerate 25mg every third day you can slowly increase it to every other day and eventually daily if you find that is the most beneficial to you
- Watch for side effects like acne, hair loss, or mood changes – this may indicate higher metabolism towards testosterone and other androgens
- If you experience symptoms such as breast tenderness, increased emotions, etc. then discontinue the use or reduce your dose as this may indicate more estrogenic metabolism
#6. Bio-identical progesterone cream (over the counter)
Another method to influence menopausal symptoms is the use of bioidentical hormones.
Many women are concerned about the potential risk of breast cancer and other issues while using bioidentical hormones after menopause.
Generally, when using the right type of hormones (meaning bioidentical) and in doses that are appropriate (low and not supraphysiologic doses), the use of these hormones does NOT result in an increased risk of breast cancer (34).
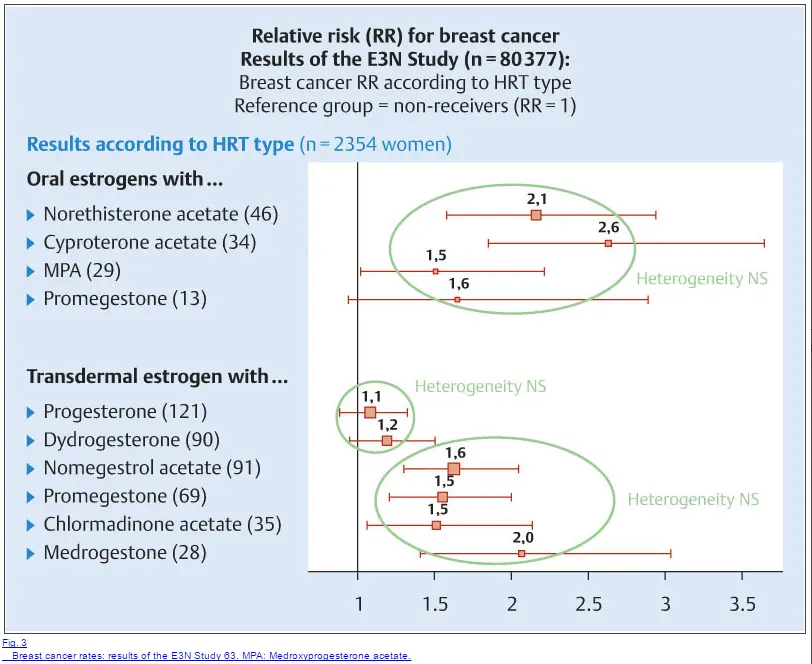
You can see from the image above that the major increased risk of developing breast cancer comes from using synthetic estrogen hormones like norethisterone acetate, etc.
Oftentimes people lump bioidentical estrogen and progesterone into the same category but they are quite different.
There is a difference between synthetic estrogens and bioidentical estrogen/progesterone.
When women go through menopause they basically have VERY little to zero progesterone in their body, while estrogen levels may fluctuate or remain high due to aromatization from fat cells.
Taking progesterone can help combat estrogen levels and may actually ease the symptoms of menopause (remember not all symptoms of menopause are due to estrogen levels).
Taking progesterone has other benefits as well including the potential to improve your sleep, help your body flush out water, increase your metabolism and improve your cardiovascular profile (35).
Like all therapies, you should make sure you research and consider all options before using supplements or hormones.
Due to various reasons, I find many women with depleted progesterone levels (starting at around age 30) which continues through menopause and into later years.
Progesterone is available over the counter (like DHEA), compared to estrogen which requires a prescription from a physician.
How to Supplement with Bioidentical progesterone
- If menstruating: Use 20-40mg per day on days 14-28 of your cycle (the latter half of the month)
- If in menopause: you can use 20-40mg per day either 6 days per week (with rest on the 7th) or 26-28 days per month (with 1-3 days off per month)
- Make sure to monitor your symptoms while using and discontinue use if you experience any negative side effects
- Discuss the use of bioidentical hormones with your physician
Wrapping it up
If you believe that you are suffering from abnormal estrogen levels make sure you get a proper evaluation.
In most cases that means getting your blood tested and then monitoring your symptoms to determine which kind of problem you have.
Most menstruating women suffer from estrogen dominance (or high estrogen levels), while menopausal women may suffer from low or high estrogen levels.
Certain supplements have been shown to alter estrogen levels by either directly changing serum estrogen levels, influencing estrogen metabolism, or enhancing other hormones that directly or indirectly alter estrogen.
Now it’s your turn:
Are you suffering from high estrogen? Low estrogen?
What have you tried?
What has worked?
Leave your comments below!
Scientific References
#1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC381441/
#2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14697301
#3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3652894/
#4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5038903/
#5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3113168/
#6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7083189
#7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15050110
#8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10938577
#9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2173856
#10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18942551
#11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2889220/
#12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22978257
#13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2967652/
#14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2889220/
#15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16357599
#16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3048776/
#17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3207614
#18. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1534735403002002005?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3dpubmed
#19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12197785
#20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2928177/
#21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18784609
#22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3614596/
#23. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3129407/
#24. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3326875/
#25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12220769
#26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25882265
#27. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14749240
#28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12220769
#29. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2783540/
#30. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3046019/
#31. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22157510
#32. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23625331
#33. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4052396/
#34. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4245250/
#35. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4245250/








