Whether you realize it or not as a thyroid patient you actually have many options when it comes to thyroid medications.
Your doctor might have you believe that the one and only thyroid medication available is Synthroid/levothyroxine but that couldn’t be farther from the truth.
There are actually many different types of thyroid medications that are FDA approved to treat hypothyroidism (1) (which means low thyroid function) and are available in the United States.
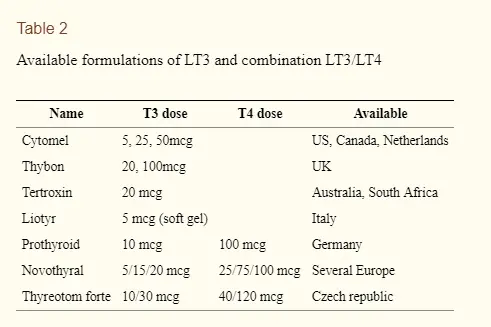
You are probably well aware of Synthroid/levothyroxine but others on this list include medications such as Tirosint, Cytomel, and liothyronine.
Article highlights:
- Compounded thyroid medications are unique among all types of thyroid medication
- You can individually titrate your T4 and T3 dose to fit exactly the demands of your body
- All medications have side effects and drawbacks but these can be minimized
- Compounded thyroid medications are available only at compounding pharmacies and require a doctor’s prescription
DOWNLOAD FREE RESOURCES
Foods to Avoid if you Have Thyroid Problems:
I’ve found that these 10 foods cause the most problems for thyroid patients. Learn which foods you should avoid if you have thyroid disease of any type.
The Complete List of Thyroid Lab tests:
The list includes optimal ranges, normal ranges, and the complete list of tests you need to diagnose and manage thyroid disease correctly!
What is Compounded Thyroid Medication
All of these medications have potential advantages and disadvantages and should always be considered!
While they are all approved to treat hypothyroidism they differ in the exact amount of hormones that they provide your body when you ingest them.
The most common thyroid medications prescribed include those which contain the most abundant thyroid hormone in your body known as T4 or thyroxine.
These medications are incredibly stable and have a long half-life but they require activation by certain enzymes in your body.
Other medications contain the most powerful and active thyroid hormone known as T3 or triiodothyronine.
T3 is incredibly potent but suffers from a short half-life and it can pack quite a kick.
The medication that I want to focus on today is one option that doesn’t get a lot of attention and it’s known as compounded T4 and T3 thyroid medication.
It’s unique among all of the other thyroid medications in that it is created only at compounding pharmacies.
These pharmacies are specialty pharmacies (very different from your standard run-of-the-mill Walgreens and CVS’s) that can formulate medications to fit your specific needs.
Instead of standardized ingredients and dosages, such as those found within levothyroxine and Synthroid, compounding pharmacies can alter the doses of each thyroid hormone component and add it to an array of binders and fillers to match what your body needs.
Unfortunately, you’ve probably never heard of compounding pharmacies because most conventional doctors (meaning those doctors who are endocrinologists and primary care providers) don’t really like these types of pharmacies.
They often believe that the formulations are not safe and may present a danger to patients due to some regulations (2).
My experience suggests that compounding pharmacies are quite safe and that there are many thyroid patients who can benefit from using compounded thyroid medications which is exactly what we will focus on today.
How Does it Compare to Other Thyroid Medications?
Compounded thyroid medications are not unlike other thyroid medications and formulations in that they all contain the same thyroid hormones.
You may not realize it but all of your thyroid medications basically contain the same two active ingredients:
- Thyroxine (known as T4)
- Triiodothyronine (known as T3)
These two thyroid hormones represent the two most biologically active thyroid hormones that your thyroid gland produces when it is healthy.
ALL thyroid medications contain one or both of these hormones in various quantities and dosages.
They also differ in the carriers, binders, fillers, and dyes found in the capsule/tablets.
It may not sound like a lot but each of these factors can and absolutely may influence how you feel when taking these medications.
Because of this, it’s important for you to at least be aware that they exist.
Why?
Because if you are someone who is not doing well on one type of thyroid medication then improving your outcome may be as simple as switching from one to another, even if they are within the same class of medications.
For instance:
Recent studies have shown that thyroid patients react differently to name brand Synthroid compared to generic levothyroxine (3).
And this same logic can be applied to compounded thyroid medications.
Compounded thyroid medications often contain both T4 and T3 and they can be dosed such that your medication provides you the same ratio that your thyroid gland produces when it is healthy.
This ratio is approximately 80% T4 and 20% T3 depending on which study you are looking at (4) and this is a great place to start when considering altering your medication.
Newer studies, such as this one from 2018 (5), support the idea that certain patients benefit from using combination medications compared to single hormone thyroid medication.
Advantages of Compounded T4 and T3 Thyroid Medication
Perhaps the greatest benefit to compounded thyroid medications is that you have the option to provide the exact dose of T4 and T3 that you want for the patient while controlling the inactive binders/ingredients that come with it.
This means that you can provide your body with quantities and dosages which are not possible with standardized thyroid medications such as Synthroid/levothyroxine.
For instance:
Let’s say that your doctor starts you on 50mcg of T4 in the form of Synthroid and 25mcg of T3 in the form of Cytomel.
Let’s assume that you are doing well on this formulation but you are not at 100%.
After looking at your labs you see that your free T3 is lower than it should be but your TSH is lower than you want it as well.
Your doctor could then adjust your medication to include 40mcg of T4 and 28mcg of T3.
This allows for the potential to alter both T4 and T3 levels simultaneously based on your thyroid lab tests.
Do you see the power here?

This sort of dosing is not available with any other type of thyroid medication because they come in standardized doses.
Beyond this primary benefit I think there are also several other benefits to using compounded thyroid medications:
- Your doctor can customize the amount of thyroid medication in each dose
- Most compounded medications contain fewer inactive ingredients and binders when compared to brand/generic thyroid medications
- Can be compounded for ‘sustained released’ which means you may not have to take multiple doses throughout the day
- Sometimes compounded medications are the only way to get T3 medication (depending on which country you live in)
Disadvantages (And Side Effects)
It’s not always sunshine and rainbows, however, as these medications do have some potential drawbacks, not unlike any other thyroid medication on the market.
Before you use any thyroid medication (or any medication in general) you should be aware of the potential drawbacks, side effects, and benefits.
Normally, your doctor should be explaining this information to you before you use it but this may not be the case given that doctors are spending less time with patients.
My recommendation is to be deliberate with your choice of thyroid medication and attempt to match your medication to your sensitivities and the needs of your body.
It’s a good idea to keep track of this information and how you feel after starting new medications with a journal.
Some disadvantages of compounded thyroid medication include:
- Does not contain other thyroid gland ingredients such as Calcitonin (6) and T1/T2 (7).
- Now always covered by insurance (may be more expensive).
- Inactive binders such as cellulose and methyl-cellulose delay absorption (8) but may result in decreased serum levels for certain people (especially those with GI issues).
- Not all compounding pharmacies have the same standards in terms of quality.
- Difficult to titrate compared to standard thyroid medication doses.
Remember:
These are potential drawbacks.
Just because you are using compounded thyroid medication does not guarantee that you will experience these consequences, but they are things you should be aware of.
Side effects of compounded thyroid medications include all of those found with other thyroid medications including:
- The risk of taking too much thyroid medication and becoming hyperthyroid (this can occur with ANY thyroid medication)
- The risk of taking too little thyroid medication and staying hypothyroid (this can occur with ANY thyroid medication)
- Direct side effects of the medication itself including things such as hair loss (this is rare but does happen)
- Direct side effects of the binders/fillers which includes symptoms such as nausea, stomach upset, indigestion, reduced medication absorption, and acid reflux.
- Hypersensitivity reactions to binders/fillers which includes symptoms such as headaches, rashes, and nausea.
How Much Does it Cost?
You will find that prices from compounding pharmacies tend to vary.
Because of this, the best way to determine how much your thyroid medication will cost (if it is compounded) is to call a local compounding pharmacy and to ask them.
You can find compounding pharmacies by searching directly on google:
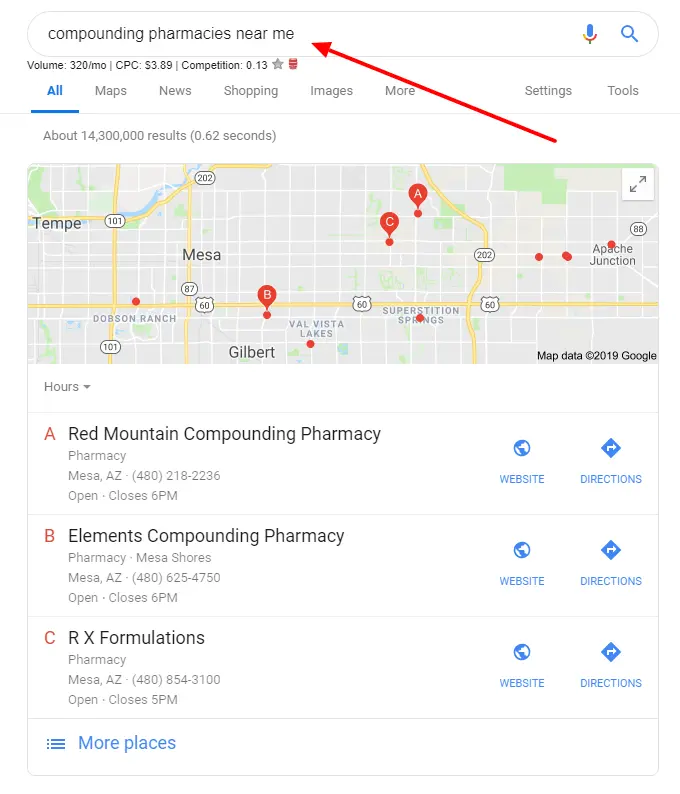
Typing “compounding pharmacies near me” should pop up several options for you to call.
You can call them directly and ask about how much it would cost to have your medication compounded.
**Related quick tip: It might be a good idea to ask the compounding pharmacy you are calling if they have any references for thyroid doctors! They often have relationships with local doctors who are more open-minded.
My own personal experience suggests that you should be able to find a compounding pharmacy which charges somewhere between $30 and $60 per month (depending on your dose and which binders they use).
You will also find that some compounding pharmacies attempt to use your insurance as well which may further reduce the cost to you.
However, be aware that this option is not available for everyone, so it’s probably more realistic to expect to pay out of pocket for this type of medication.
My opinion is that it’s worth the potential loss of $30-$60 if it means dramatically improving your overall health and reducing your hypothyroid symptoms.
I find that most people who use compounded thyroid medications often feel better on these medications when compared to standard thyroid medication such as Synthroid.
This is not a universal truth, but it tends to be true for most people.
How to Get Compounded Thyroid Medication
Compounded thyroid medication, like other thyroid medications, is only available with a prescription from a doctor.
This may not be true for everyone reading this as some of you come from countries where you can pick up prescription medications over the counter but if you are in the United States then it will require a prescription from a licensed doctor.
But just because you have a current doctor does not necessarily mean that they will be willing to write you a prescription for compounded thyroid medication.
As I stated previously, some doctors do not believe that compounding pharmacies are safe (despite the fact that thousands of thyroid patients use their medications on a daily basis).
The only way to determine if your doctor is willing to prescribe this medication is to simply ask them.
If you find that they are unwilling to prescribe anything other than Synthroid or levothyroxine then it may be time to seek a second opinion or look for a doctor who is more willing to work with you and your situation.
Hypothyroidism is not a one-size-fits-all type of disease.
Each patient will require a different approach to management and part of that management includes different types and doses of thyroid medication.
If you are having trouble finding a doctor who is willing to work with you be sure you check out this free resource which is designed to help you find a local thyroid literate doctor.
Conclusion
Compounded thyroid medication is one of many types of thyroid medications available in the United States.
It contains some specific benefits which are unique to this class of thyroid medication and not shared with other thyroid formulations.
Despite these benefits, however, not everyone will necessarily need compounded thyroid medication from their doctor.
Before you decide to use it be sure you check out the potential benefits and side effects and weigh those options for your specific situation.
Now I want to hear from you:
Are you someone who is currently taking compounded thyroid medication right now?
If so, how are you doing on it?
Have you taken it in the past? If so, how was your reaction and why aren’t you taking it now?
Please share your questions or comments as they can help future thyroid patients figure out what is optimal for their body.








