Natural desiccated thyroid is a thyroid medication that comes from pigs!
This medication contains a more “complete” profile of thyroid hormones when compared to almost all synthetic thyroid medications out there.
This has led many people to tout NDT as the “best” thyroid medication.
In this article, we are going to explore this claim while also discussing the pros and cons of this medication.
You’ll learn who should use this medication, who should avoid it, and the pitfalls of using it.
Let’s dive in:
What is NDT or Natural Desiccated Thyroid Hormone?
NDT or natural desiccated thyroid hormone is simply a type of thyroid hormone medication.
It can be used to treat people who have low levels of thyroid hormone in their body from conditions like Hypothyroidism and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
NDT is often claimed to be one of the “best” thyroid medications out there because it’s considered to be all-natural.
So, with this in mind, let’s break apart what NDT actually is.
First:
Where does NDT come from?
NDT is porcine-derived which means that it comes from pigs. (1)
To get NDT, people must take the thyroid gland of pigs and desiccate or dry it out.
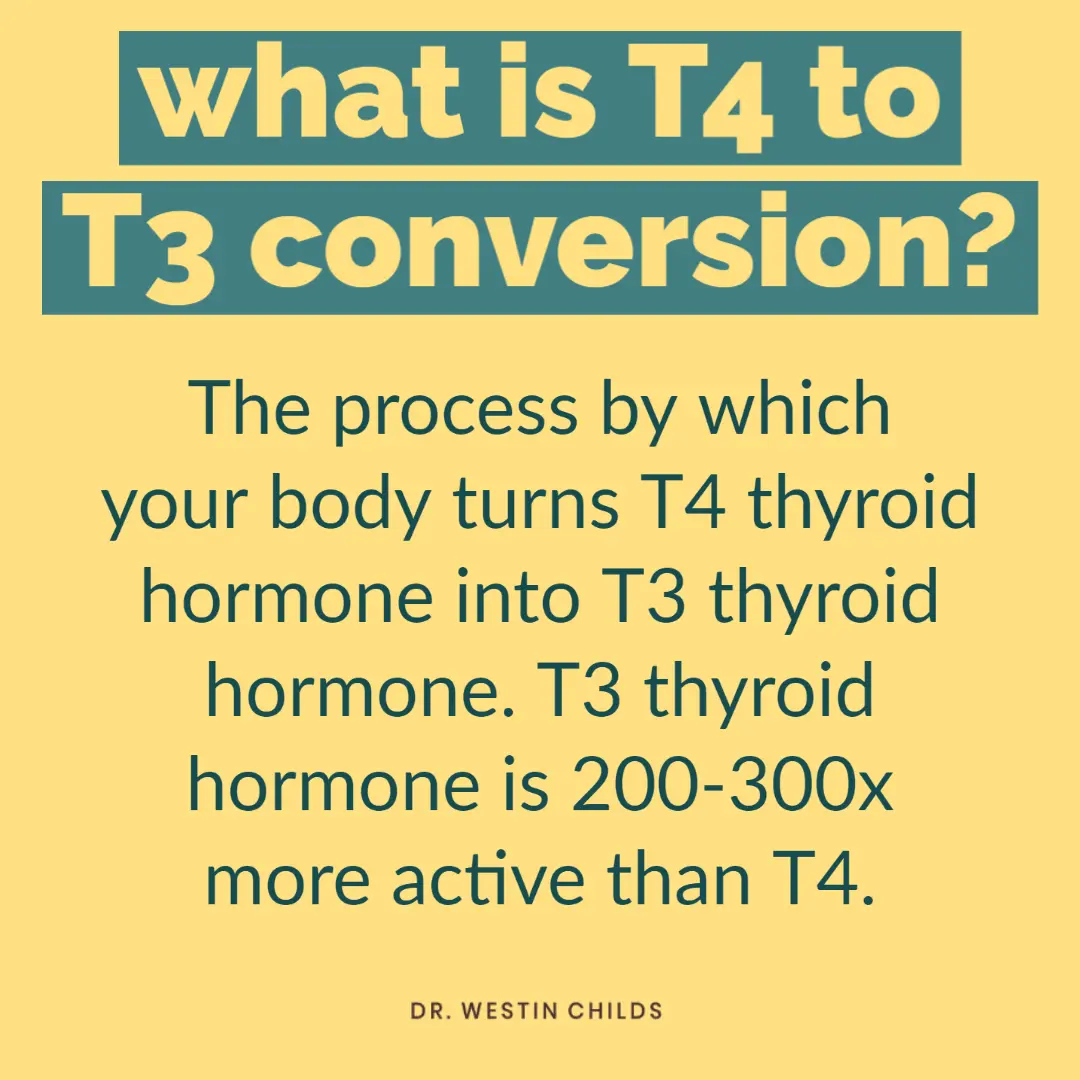
From there it is standardized to a specific dose and contains 38mcg of T4 (the inactive thyroid hormone) and 9mcg of T3 (the active thyroid hormone) in each grain.
Grain is just a way to standardize the dose of NDT between different brands.
Natural desiccated thyroid also contains other hormones and prohormones such as other types of thyroid hormone (T1 and T2).
These hormones are not nearly as active as T4 and T3 but they are thought to play an important physiologic role in the body otherwise, (2) why would your body produce them?
Each grain of NDT contains around 76% T4 and around 23% T3 which is a ratio close to the 80% T4 and 20% T3 that your thyroid produces naturally when it is healthy.
For this reason, and because it contains prohormones, and because it comes from a natural source, (3) many people believe it is one of the most complete thyroid medications out there!
While this may be true, it doesn’t mean that it works equally well for every single person.
Let’s dig into the basics of NDT and talk about why it may not be the best medication.
DOWNLOAD FREE RESOURCES
Foods to Avoid if you Have Thyroid Problems:
I’ve found that these 10 foods cause the most problems for thyroid patients. Learn which foods you should avoid if you have thyroid disease of any type.
The Complete List of Thyroid Lab tests:
The list includes optimal ranges, normal ranges, and the complete list of tests you need to diagnose and manage thyroid disease correctly!
Natural vs Synthetic Hormones
NDT is considered to be natural because it is sourced from a “natural” source, pigs.
This sourcing of thyroid hormone is different from the approach used to create other formulations of medications such as Levothyroxine and Synthroid.
Other medications are created in a laboratory from other basic compounds. (4)
But you must always remember that ALL types of thyroid medications are considered to be bio-identical which is very important.
Bio-identical means that the hormones you are taking by mouth are considered to be IDENTICAL to the hormones that your body produces naturally!
Where these medications differ is in the SOURCE.
The source for NDT is from pigs while the source for Levo and Synthroid is other chemical structures.
Some people believe that naturally sourcing thyroid hormone is superior to creating it chemically in a lab.
From my perspective, there is no difference between thyroid hormone from a human or a pig when compared to thyroid hormone created in a lab.
Both compounds look the exact same and function in a similar way in the body.
Where they differ is in the other hormones and pro-hormones that come in NDT formulations.
NDT Brands
Let’s take a second to discuss the various brands of natural desiccated thyroid hormones out there.
There are several “well-known” brands and some less well-known brands.
What you need to understand is that these medications do differ in the type of active and inactive ingredients in them but they all contain both T4 and T3 thyroid hormones.
While it may not sound like the inactive ingredients make a big difference, they actually may be the reason that some people simply can’t tolerate certain types of NDT brands.
For instance:
It’s not uncommon for someone to be on Armour thyroid but not feel well when switching to Nature-throid or WP thyroid even if their dose stays the same.
These differences are likely the result of how your body interacts with the inactive ingredients and how difficult it is for your intestines to break down and absorb the hormones in the medication.
What that means for you is that if you don’t tolerate one type of NDT brand it doesn’t mean you won’t tolerate all of them.
Instead, you may want to switch to a couple of different brands to see if you can find one that works for you.
With that in mind you can find a list of NDT brands below:
- Armour Thyroid
- WP Thyroid – Has the fewest inactive ingredients
- Nature-Throid
- NP Thyroid
- ERFA
- Whole thyroid
- And other names based on the Country you live in
Is NDT Superior to T4 Medication for Hypothyroidism?
It is largely felt by many online communities that natural desiccated thyroid is the single “best” thyroid medication out there.
This logic has led people to believe that if you are taking NDT and it isn’t working for you that the problem must be with your dose and not with the medication itself.
I’m not a fan of this approach and don’t believe that when it comes to your thyroid that there is a single “best” thyroid medication.
A better approach is to always listen to your body while you look at other problems beyond your thyroid.
Thyroid tunnel vision can lead you to believe that every problem you have is associated with your thyroid and that adjusting your dose is the solution to this problem.

This approach to management has led many patients to take higher than necessary doses of thyroid medication which can be dangerous!
So, while NDT is a great medication, it’s certainly not the “best” or the only thyroid medication available.
The type of thyroid medication that you use, and your dose, should be individualized to YOUR body.
Natural Desiccated Thyroid for Weight Loss
One important note worth mentioning is that of weight loss and NDT.
This particular study took a look at 70 patients that were already taking T4 medication (Levothyroxine).
This group of patients was taking this medication and despite having a normal TSH still had some symptoms of hypothyroidism.
These patients were then randomized and given NDT (desiccated thyroid extract) for 16 weeks and then placed back on their old medication.
During the period that these patients were taking NDT, they noticed around a 3-pound weight loss on average and roughly 50% of patients taking NDT wanted to stay on it.
Not only did they lose weight but they also reported feeling much better on the medication in a subjective sense (based on their own opinion).
3-4 pounds may not sound like a big deal to you, but when you realize that weight is incredibly difficult to lose when you have hypothyroidism this is actually a great feat.
But does this mean that the weight loss is due to NDT itself or simply due to the T3 in the medication?
While we don’t have definitive studies, it’s logical to believe that the same results would have been achieved by simply adding T3 (in the form of Cytomel or Liothyronine) to existing doses of T4 in these patients.
So, while NDT can certainly help you lose weight if you have hypothyroidism, don’t fall into the trap of believing that the weight loss is caused by the NDT itself.
Instead, the weight loss is most likely the result of IMPROVING the total T3 and free T3 levels in your body!
And this can be done with T3 medication of any type. (6)
Common Problems and Symptoms when using NDT
Let’s talk about some of the problems associated with NDT use.
The way that your body responds to NDT is going to be different from other people out there.
This means that the type of NDT that you use, and the dose that you use, all may potentially lead to problems.
What’s important is to focus on how YOU feel and how YOU tolerate the medication.
By listening to your body, and by checking your thyroid lab tests, you can be certain that you are taking the right dose for your body.
You can find a list of the most common problems that patients experience when they use NDT below:
- Some people take too much natural desiccated thyroid hormone – (7) Overdosing on NDT is a common problem because many people believe that higher doses will somehow improve their thyroid function. This leads to overdosing and symptoms of hyperthyroidism in some patients. This problem stems from “thyroid tunnel vision”.
- Dosing is static which means you can’t tweak the T4 and T3 concentrations – NDT comes in a static dose of 38mcg:9mcg of T3. This means that you can’t individually adjust the amount of T3 in the medication without also adjusting the T4. You might do great on 38mcg of T4 but may need something like 5mcg of T3. If you fall into this category then you can’t adjust your medication.
- May lead to variations in free T3 & Free T4 levels – Some people experience very high free T3 levels and very low free T4 levels even when using low doses of NDT. This problem probably has to do with how each individual processes thyroid hormone in their body.
- Symptoms arise from the use of T3 which can be difficult to manage in some patients – (8) Some patients are exquisitely sensitive to even incredibly low doses of T3. These are patients that would probably do fine on certain types of T4 medication (such as Tirosint) but do poorly when they start even low doses of NDT.
- May be hard to break down for some patients in the intestines – This problem isn’t unique to NDT medications, but it’s worth considering if you have intestinal issues. Inactive dyes and fillers may cause reactions and may make the digestion of NDT difficult.
- May lead to immunogenic reaction (may not be ideal for patients with Hashimoto’s) (9) – There is a theoretical risk that taking a foreign pig-derived substance can “flare” up the immune system and worsen thyroid function in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. I don’t think this is a reason to completely avoid NDT if you have Hashimoto’s thyroiditis but you should be aware that it can happen.
Overdosing on NDT
Believe it or not but doctors have been using NDT since the 1950s!
This was way before thyroid lab tests were created, so dosing was often based on the “Basal metabolic rate” which is a marker for metabolism.
These doctors found that increasing the dose of NDT did result in modest weight loss by increasing the metabolism, but once the dose was lowered, the metabolism of the patient went back down to below-normal levels.
This is as relevant today as it was back then.
Currently, many people believe that by simply increasing their dose of NDT that they will finally feel better and relieve their symptoms.
This happens frequently in patients who are suffering from weight gain.
This leads to higher and higher doses of NDT which dramatically suppresses the TSH and temporarily helps with weight loss.
But the unintended effect is that it may also cause long-term harm because of the high dose of NDT being used.
If you are still feeling symptomatic at that point then some of your symptoms are likely related to some other problem or some other hormone imbalance!
You can avoid these potential negative side effects by using only the appropriate dose and by monitoring your thyroid lab tests in the process.
Who should use NDT
NDT is a great medication and many people out there stand to benefit from its use.
I’ve compiled a list of just some of the patients that tend to do the “best” on this medication below:
- Those who have failed T4 medication – If you’ve been on T4 medication such as Levothyroxine or Synthroid and you just aren’t feeling well after 6-8 weeks then it may be time to consider a T4/T3 combo medication.
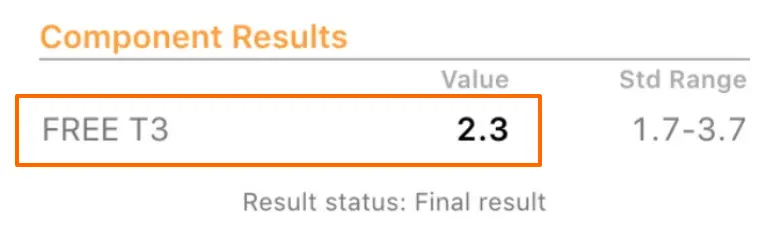
- Those with low free T3 levels (usually need a T3 medication) – Up to 15% of the population suffers from thyroid conversion issues which means they don’t convert T4 into T3 as well as other people. If you fall into this category you may have a “normal TSH” but your free T3 and total T3 levels may be lower than normal. If you fall into this category then adding T3 (from either NDT or Liothyronine) may help bring these levels up and help you feel better.
- Those who are post-thyroidectomy – Your thyroid (when functioning normally) produces around 80% T4 and around 20% T3. If you don’t have a thyroid, because it was removed or destroyed, then it makes sense to supplement with thyroid hormones close to this ratio. Most post-thyroidectomy patients take only T4 medications (so 100% T4) which do not contain T3. Some of these patients don’t feel well despite having a normal TSH. Taking NDT can provide your body with T3 in a ratio that is close to what your body produces naturally and may help those without a thyroid. (12)
This is not an all-inclusive list but it can help get you started!
Conclusion
Natural desiccated thyroid is a thyroid medication that contains both T4 and T3.
Because of this, it may be one of the better thyroid medications (but not the best!) out there.
If you have thyroid issues and are struggling with low free T3 levels, weight gain, and/or other symptoms despite having a normal TSH, then this medication may help you.
When using it be careful to watch for side effects such as anxiety, heart palpitations, or hot flashes which may indicate that your dose is too high.
Now I want to hear from you:
Are you taking NDT? Is it working for you?
Are you not tolerating NDT?
Is it causing negative symptoms?
If so, leave your comments or questions below!
I’ll do my best to respond to each comment.