Hypothyroidism is very common among people in the US which means that many people are taking thyroid hormones.
Despite taking thyroid hormones, many patients still show the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Why is it that some patients who take thyroid hormone replacement medication for low thyroid still have symptoms?
In this post I will explain the top 10 low thyroid symptoms and explain how low thyroid causes each of these symptoms:
Why do doctors miss low thyroid symptoms?
Hypothyroidism (meaning low thyroid function in the body) is incredibly common in the US.
But more important than that there are a number of unhappy hypothyroid patients
It is estimated that up to 10% of people have what is known as subclinical hypothyroidism (1).
Subclinical hypothyroidism is meant to refer to a condition where the TSH is elevated, but not quite where doctors would qualify the patient as having true hypothyroidism.
Often patients who are diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism are not treated with thyroid hormone until their TSH reaches a certain point.
It is this reliance upon TSH that may explain why so many hypothyroid patients are unhappy and left very symptomatic.
Take for instance patients with subclinical hypothyroidism.
When you compare the symptoms of patients with subclinical hypothyroidism to euthyroid (meaning patients without hypothyroidism) you see a stark difference:
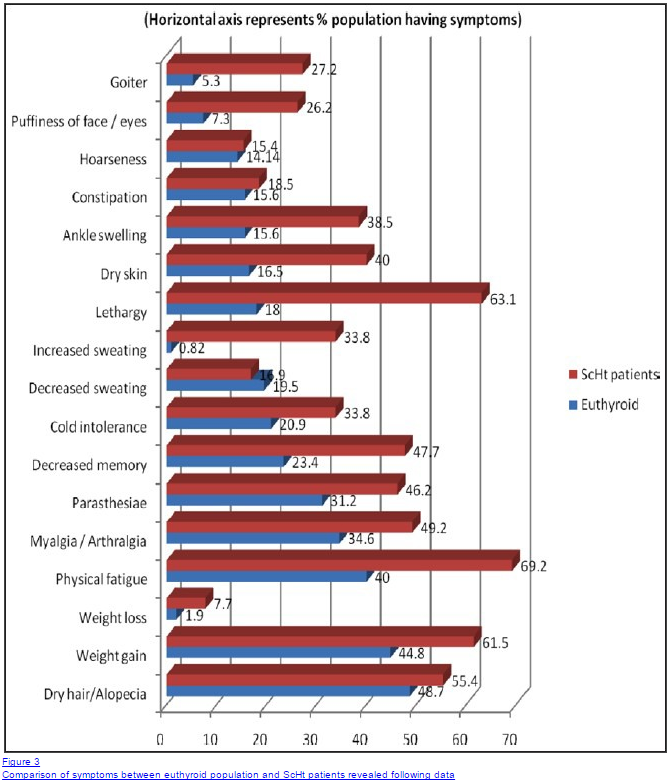
Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism display a number of hypothyroid symptoms ranging from weight gain to cold intolerance, to physical fatigue and more.
What’s more important is that all of these symptoms directly coincide with the true symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Begging the question:
Does subclinical hypothyroidism help explain why so many patients are undertreated and remain hypothyroid?
In part, I think it may explain some of it, but another huge part of the equation is the reliance upon TSH testing as the ultimate diagnostic tool.
Many providers use TSH testing as a means to diagnose thyroid function and use the TSH to determine if and how much thyroid hormone a patient needs.
This occurs despite the fact that some conditions make the TSH test less reliable.
And it occurs despite the fact that studies have shown that hypothyroid patients being treated based on the TSH have lower T4 and T3 levels (and more weight gain and lower metabolisms than age-matched controls).
As a result of the current paradigm of treatment, many patients are left feeling like their symptoms may be “in their head” or due to some other cause.
Let’s break down how low thyroid function can cause these symptoms and explain why you feel the way you do:
DOWNLOAD FREE RESOURCES
Foods to Avoid if you Have Thyroid Problems:
I’ve found that these 10 foods cause the most problems for thyroid patients. Learn which foods you should avoid if you have thyroid disease of any type.
The Complete List of Thyroid Lab tests:
The list includes optimal ranges, normal ranges, and the complete list of tests you need to diagnose and manage thyroid disease correctly!
#1. Unexplained Weight Gain
One of the main symptoms of hypothyroidism is unexplained weight gain.
We all know that this is a symptom of hypothyroidism, it’s a classic symptom and one that is confirmed by every major and conventional establishment (2).
But here is the interesting thing:
If hypothyroidism causes weight gain, then why doesn’t replacing thyroid hormone with Synthroid or levothyroxine cause weight loss? (in the majority of patients)
Why is it that patients who have their thyroid taken out gain around 15-20 pounds on average despite being treated with thyroid hormone to a normal TSH?
Either we don’t really understand the true function of thyroid hormone in the body, or we don’t understand how to replace thyroid hormone correctly… or both.
I think it’s really a combination of both and it’s something I’ve explained in detail here.
The truth is that thyroid hormone impacts other hormones in your body that directly regulate your fat cells and how your body burns fat.
Thyroid hormone (T3 specifically) has a direct effect on hormones like leptin and insulin.
Together these hormones determine how many calories you are going to burn, what your metabolism is going to be, and how your body will distribute and place fat on your body.
Low levels of thyroid hormones potentiate a condition known as insulin resistance (3).
It also potentiates leptin resistance (4).
It is the low thyroid states which create these other hormone imbalances that then lead to weight gain and the inability to lose weight.
The main problem is simply taking thyroid hormone may improve your thyroid status but does not directly influence these hormones which is why most patients do NOT lose weight when starting thyroid hormone.
#2. Inability to lose weight despite changing your diet and exercising more
Another huge problem is the fact that many patients with hypothyroidism can’t lose weight despite actually trying.
I know from experience that many hypothyroid patients are out there exercising 5+ times per week, they are eating as few as 1,000 calories per day and they still aren’t losing weight.
They are left confused when they go to the doctor only to have the doctor recommend that they either must be lying or they simply are not exercising hard enough.
I have to point out that the concept of reducing your calories and exercising more has not been shown to actually result in long-term weight loss.
So pushing the eat less/exercise treatment paradigm simply will not work (but it especially won’t work for hypothyroid patients).
We have studies like the biggest loser study (5) which outline exactly what happens with calorie restriction and lots of exercises.

Reducing your calories results in a reduction in your basal metabolic rate that persists for YEARS.
Contestants of the biggest loser showed that on average they were burning less than 700 calories per day than what was expected.
This effect lasted at least 6 years (and probably more).
How does this fit in with your thyroid?
Your thyroid helps to directly regulate your basal metabolic rate which is the most important factor when determining if you will lose weight and keep it off.
Low thyroid hormone results in a lower basal metabolic rate by reducing energy production and regulating key enzymes in your mitochondria.
Low thyroid hormone = low metabolism PLUS hormone imbalances noted above which results in weight loss resistance.
So, no, the inability to lose weight is NOT in your head and is a result of biochemical changes in your body mediated by low thyroid hormone.
#3. Crushing fatigue or low energy levels
Fatigue and low energy are another one of those symptoms that is very common among hypothyroid patients.
Low energy levels results from the same mechanism that regulates your metabolism:
Energy production in the mitochondria.
ATP is the energy currency in your body and it is created from your mitochondria.
Adequate ATP is required for normal functions like muscle contraction, neurologic impulses, etc.
Low levels of thyroid hormone result in a reduction in mitochondrial energy production (6).
This isn’t the only way that hypothyroidism causes low energy, however.
In addition to influencing your energy production thyroid hormone also impacts other hormones that regulate energy levels like cortisol.
Low thyroid hormone also causes issues with cortisol which can lower energy levels as well (7).
#4. Unexplained hair loss
Hypothyroid patients often complain about changes to their hair quality and texture. In addition, many hypothyroid patients also experience significant hair loss.
These changes happen for 2 main reasons:
First:
Thyroid hormone has a direct influence on your hair follicles and stimulates hair production.
Second:
Thyroid hormone is required for optimal nutrient absorption and low thyroid hormone sets you up for developing nutrient deficiencies like low iron and B12 deficiency.
Both iron and B12 are required for proper hair growth.
This is another situation where replacing thyroid hormone may not improve your hair loss unless you ALSO address the underlying nutrient deficiencies.
I’ve written about thyroid hair loss and all of the factors that go into this subject which you can read here.
To elaborate here optimal ferritin is required for proper hair growth, in fact, you need at least 30ng/ml to have “normal” hair growth.
Unfortunately, slight changes to your ferritin levels can be missed if they are not closely evaluated which may leave patients with hair loss despite being on thyroid medication.
#5. Menstrual irregularities
Many patients who suffer from low thyroid also endorse changes to their menstrual cycles or symptoms such as PMS and/or PMDD.
In addition, one common reason for infertility and miscarriage is hypothyroidism.
So how does thyroid hormone impact these things?
Thyroid hormone plays a very important regulatory role in balancing progesterone and estrogen.
In hypothyroid states (meaning low thyroid hormone) women tend to have low progesterone and higher than-normal estrogen levels.

This change in balance is known as estrogen dominance and this hormonal imbalance leads to conditions such as PMS, PMDD, fibrocystic breast disease, endometriosis, etc.
Having low thyroid hormone in your body reduces the chance that you will ovulate (8) and increases the chance that you will have an anovulatory cycle.
Thyroid hormone also helps to stimulate the release of progesterone.
This means that low thyroid hormone results in low progesterone directly and also indirectly alters progesterone levels by reducing the chance of ovulation.
These changes result in menstrual irregularities and infertility.
#6. Changes in mood including depression or anxiety
There is a very big connection between alterations in thyroid hormone in the body and changes in neurological function.
Most commonly this manifests as depression in low thyroid states.
The exact reason for this isn’t well understood, but the connection between them is very clear (9).
Because of this connection, many studies show that augmenting standard treatment with thyroid hormone has been shown to reduce depression significantly.
In other studies adding T3 to patients with bipolar disorder has been shown to reduce symptoms in up to 80% of patients (10) (these are patients who have failed traditional medications).
Surprisingly these patients didn’t have very many negative side effects.
Other studies have shown that up to 50% of patients with depression improve significantly when adding as much as 500mcg of T4 (11) to their regimen each day.
Despite being on such high doses of thyroid medication these patients did not have negative side effects.
The point is that many cases of depression may actually be caused by hypothyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism that is being misdiagnosed as depression.
#7. Changes to other hormone systems in the body
A recurring theme in this post is how the thyroid hormone impacts many other hormone systems in your body.
In this section I want to outline the specific hormones and how thyroid hormone impacts them (specifically low thyroid hormone):
- Testosterone – Low thyroid hormone makes testosterone levels lower than normal resulting in weight gain, depression, and a reduction in metabolism.
- Insulin – Low thyroid hormone results in insulin resistance which exacerbates weight gain and makes weight loss difficult.
- Leptin – Low thyroid hormone results in leptin resistance which alters basal metabolic rate and increases appetite dramatically.
- Cortisol – Low thyroid hormone results in higher than normal cortisol levels and therefore low energy levels.
- Progesterone – Low thyroid hormone results in low progesterone which leads to imbalances in the estrogen/progesterone ratio and may cause estrogen-dominant conditions and symptoms.
The main point here is that these other hormone imbalances are a RESULT of low thyroid hormone in the body and simply taking thyroid hormone may not be enough to completely reverse these conditions.
These hormone imbalances may, in part, explain why so many hypothyroid patients still have difficulty with weight loss and low energy levels despite taking thyroid hormones.
#8. Chronic pain or muscle tenderness
This is a symptom that many patients may are not aware is connected to their thyroid.
And it works like this:
In your body ATP (the unit of energy) is required for muscle RELAXATION, not muscle contraction.
So your muscles have the ability to contract with or without sufficient energy, but they need ATP to relax and go back to normal.
In lower-than-normal energy states, some muscles can become contracted, even in small places, resulting in “trigger points” or “balls of muscle tension”.
These areas are very sensitive to the touch, and cause extreme pain when pressed on.
Providing thyroid hormones allows the body to produce enough energy in the form of ATP to relax these tense muscles which can result in a reduction in whole-body pain and muscular tension.
Through this connection, it has even been suggested that some cases of fibromyalgia are caused by a condition known as tissue-level hypothyroidism (12).

The treatment for this condition is, of course, to replace thyroid hormone in the body and to get rid of the trigger points through various means.
#9. Cold hands/feet or lower-than-normal body temperature
Your body produces heat by creating and burning energy.
ATP production and mitochondria are involved in this process.
The more energy that you produce and consume the higher your body temperature will be.
Low states of thyroid hormone reduce the total amount of energy that you produce which reduces the heat that you produce which results in low body temperature.
This process, known as thermogenesis (13), is also closely related to your metabolism.
The higher your basal metabolic rate (remember which is influenced greatly by thyroid hormone) the more energy that you will burn at rest: breathing, eating, thinking, sleeping, etc.
The more energy you burn doing these basic tasks the higher your metabolism will be and the easier it will be to lose weight.
Your metabolism represents over 90% of the calories you burn and that is why it is the single most important factor for weight loss.
#10. Constipation or changes to bowel movements
Thyroid hormone is also directly involved in the kinetics of your bowels.
Put in more basic terms this means that thyroid hormone helps your gastrointestinal tract move normally.
Your GI tract, whether you realize this or not, is always moving in a slow rhythmic contraction known as peristalsis.
Thyroid hormone helps this peristaltic motion (14) and allows for proper transit time, proper nutrient absorption, and normal bowel movements.
The low thyroid state slows down the rate at which your bowels move and increases the risk of developing overgrowth conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and small intestinal fungal overgrowth.
The connection between SIBO and hypothyroidism is quite strong and as many as 50% of hypothyroid patients have been shown to test positive for SIBO (15).
Hypothyroidism also directly results in constipation due to these effects.
And remember, persistent symptoms of constipation should go away with thyroid hormone replacement!
Why do hypothyroid patients on thyroid medication still have side effects?
If you are taking thyroid medication and still having side effects then an obvious question is why is that the case?
When you learn how thyroid hormone affects each system in your body it’s easy to understand why thyroid hormone is so critical.
Part of this problem has to do with our current treatment paradigm which puts all of the importance of thyroid hormone management on one test: TSH.
It makes sense that we should evaluate different ways to manage and treat hypothyroidism if so many hypothyroid patients still exhibit the symptoms of hypothyroidism despite being treated with thyroid hormone.
In fact, you can read more about different ways to manage and treat hypothyroid patients in these posts:
- The importance of reverse T3 for testing and treating hypothyroid patients
- How to lose weight with hypothyroidism
- How using T3 can help with weight loss
- How levothyroxine can contribute to weight gain
- How to properly take thyroid medication
Use these resources to help you understand how thyroid hormone functions and how to get proper treatment so you can reduce these symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism FAQ:
If you still have questions regarding your thyroid and symptoms please see the FAQ below.
What are the causes of hypothyroidism?
The most common cause of hypothyroidism in the US is an autoimmune condition known as autoimmune thyroiditis.
This condition results in inflammation and autoimmunity which eventually destroys the thyroid gland and results in reliance upon thyroid hormone replacement.
This is not the only cause of hypothyroidism, however.
Low thyroid function can also be caused or exacerbated by nutrient deficiencies (such as iodine), uptake of endocrine-disrupting chemicals, exposure to heavy metals, extreme stress (physiologic), and even extreme weight loss or a history of recurrent yo-yo dieting.
Can hypothyroidism make you feel dizzy?
Yes, hypothyroidism can cause issues regarding balance and lead to symptoms such as dizziness or lightheadedness.
Taking thyroid hormone replacement can also cause and exacerbate these symptoms as well.
Can nausea be a symptom of hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism can indirectly cause nausea.
This is mediated through thyroid hormones’ effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Low thyroid states may result in a condition known as reduced gastric emptying or even symptoms such as acid reflux which manifests as nausea.
Can a sore throat be a sign of thyroid problems?
Typically a hoarse throat or the sensation of swelling in the throat is attributed to inflammation and may be a sign of autoimmune thyroiditis.
Remember that not all cases of hypothyroidism are caused by autoimmune thyroiditis but it is the most common cause.
If you are having persistent swelling in the throat or neck you need further evaluation including a thyroid panel.
Why do I have hypothyroidism?
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis.
If you have hypothyroidism it is worth evaluating your antibody levels to determine if this is the reason for hypothyroidism in your body.
You can also check various nutrients to determine if they are contributing to your thyroid function as well.
Can stress cause thyroid problems?
Yes, chronic stress has been shown to trigger and worsen autoimmune diseases and chronic physiologic stress can alter (lower) thyroid hormone production and blunt T4 to T3 conversion.
Can your thyroid alter your cholesterol?
Yes, it is well known that hypothyroidism results in high cholesterol (16).
Some studies recommend routine testing for thyroid function in all patients with abnormal lipid (cholesterol) profiles because of this connection.
Taking thyroid hormone, if you are deficient, will help normalize cholesterol levels.
What is the cause of high TSH levels?
High TSH is generally a result of low circulating of thyroid hormones in your blood which then feeds back to your pituitary which results in an increased TSH.
TSH can also become elevated due to low thyroid hormone production from the thyroid gland due to a variety of reasons.
If you have a high TSH your first step should be checking your thyroid antibodies and evaluating the basic nutrient status in your body.
Can hypothyroidism be cured?
If your hypothyroidism is caused by something that is reversible and preventable then the answer is a potential yes.
For instance, providing a patient who is low in iodine with iodine results in a dramatic improvement in thyroid function.
However, cases such as chronic autoimmune thyroiditis may result in chronic glandular damage to the thyroid gland over time.
How do you diagnose hypothyroidism?
It is best to order a complete thyroid lab panel which includes much more than the traditional TSH test.
The complete panel includes TSH, free t3, free t4, reverse t3, thyroid antibody levels, and sex hormone-binding globulin.
You can read more about the best thyroid tests and how to interpret them here.
What does it mean to have an underactive thyroid?
An underactive thyroid refers to having low levels of thyroid hormone circulating in your body.
An underactive thyroid is often meant to imply that you have hypothyroidism or reduced thyroid function in the body.
Low thyroid hormone results in weight gain, fatigue, hair loss, etc.
You can find a complete list of thyroid symptoms here.
Which type of thyroid problem causes weight gain?
Having LOW thyroid function in your body results in weight gain.
Other terms used for this condition include an underactive thyroid, low thyroid function, and hypothyroidism.
All of these terms are meant to imply that your body does not have enough thyroid hormone in circulation.
Now it’s your turn:
Are you suffering from these symptoms of having a low thyroid?
What kind of treatment has worked for you? What hasn’t?
Leave your comments below!








